Unlocking Efficiency and Profitability: How ERP Software Transforms Manufacturing Businesses
 .
.
Welcome to the world of manufacturing, where efficiency reigns supreme, and every minute counts. In this dynamic environment, where intricate processes and complex supply chains intertwine, finding the right tools to optimize operations is paramount. Enter ERP software, a game-changer that can revolutionize your manufacturing business, from production planning to inventory management and beyond.
Imagine a system that seamlessly connects all your business functions, providing real-time insights into your operations. This is the power of ERP software, a centralized hub that streamlines processes, eliminates redundancies, and empowers you to make data-driven decisions. But how does it actually work? And what are the specific benefits it offers for manufacturers?
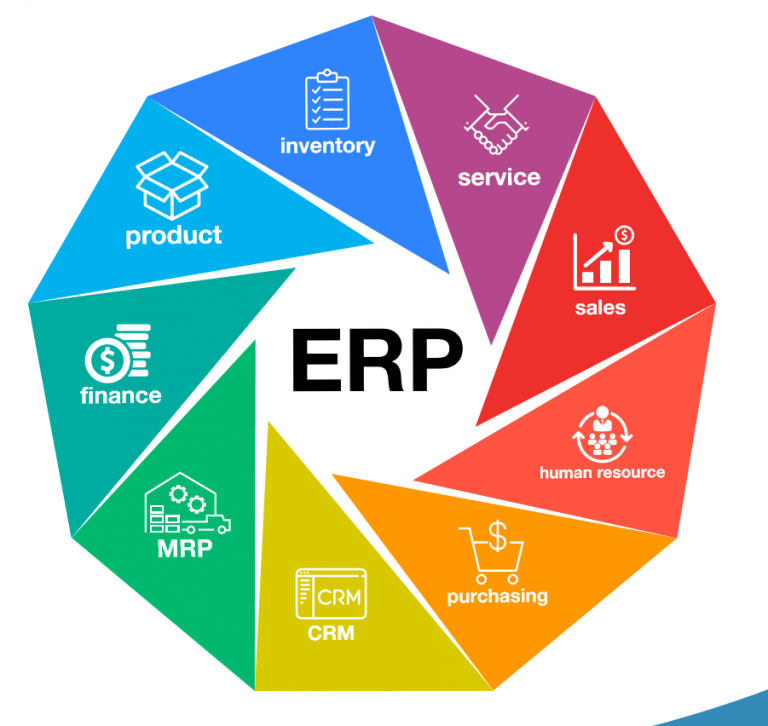
ERP software acts as the central nervous system of your business, integrating various departments and functions under one unified platform. This integration eliminates silos, fosters collaboration, and ensures data consistency across the entire organization. From sales and marketing to production, finance, and human resources, ERP software connects every aspect of your business, enabling seamless information flow and real-time visibility.
For manufacturers, the advantages of ERP software are manifold. It streamlines production planning, optimizes inventory management, improves supply chain visibility, and enhances customer service, ultimately driving profitability and efficiency. But the journey to ERP implementation is not without its challenges. Choosing the right software, integrating it with existing systems, and training your workforce are crucial steps that require careful planning and execution.
 .
.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of ERP software for manufacturing, exploring its functionalities, benefits, challenges, and best practices. We’ll navigate the complex landscape of ERP solutions, providing insights into the key features, implementation strategies, and potential pitfalls to help you make informed decisions for your manufacturing business.
Unlocking the Power of ERP Software: A Deep Dive into Manufacturing Efficiency
1. Streamlining Production Planning: From Chaos to Control
Production planning is the backbone of any manufacturing operation, determining the flow of materials, resources, and labor to meet production targets. In the absence of a robust system, production planning can become a logistical nightmare, riddled with inefficiencies, delays, and wasted resources. This is where ERP software steps in, transforming production planning from a chaotic process to a streamlined and efficient operation.
Real-time Visibility and Data-Driven Decisions:
ERP software provides real-time visibility into production schedules, material availability, and resource utilization. This allows manufacturers to monitor progress, identify bottlenecks, and adjust production plans proactively. Data-driven insights empower decision-making, enabling manufacturers to optimize resource allocation, minimize downtime, and ensure timely delivery of products.
 .
.
Automated Scheduling and Capacity Planning:
ERP software automates scheduling tasks, eliminating manual errors and ensuring efficient allocation of resources. Advanced capacity planning tools allow manufacturers to assess production capacity, identify potential bottlenecks, and optimize resource utilization. By automating scheduling and capacity planning, ERP software frees up valuable time for production managers to focus on strategic initiatives.
MRP (Material Requirements Planning):
ERP software incorporates MRP, a powerful tool for managing materials and ensuring that the right components are available at the right time. MRP analyzes production plans and generates material requirements, ensuring timely procurement and minimizing inventory holding costs. By automating material planning, ERP software streamlines the supply chain and reduces the risk of production delays.
Production Tracking and Reporting:
 .
.
ERP software provides comprehensive production tracking capabilities, allowing manufacturers to monitor progress, identify deviations, and analyze production performance. Real-time data on production output, downtime, and quality metrics enables manufacturers to identify areas for improvement and optimize production processes. Detailed reports provide valuable insights into production efficiency, helping manufacturers identify bottlenecks and optimize resource allocation.
Benefits of ERP for Production Planning:
- Reduced production delays: Real-time visibility into production schedules and material availability minimizes delays and ensures timely delivery of products.
- Optimized resource allocation: Data-driven insights enable manufacturers to allocate resources efficiently, minimizing waste and maximizing productivity.
- Improved production efficiency: Automated scheduling, capacity planning, and MRP tools enhance production efficiency, reducing downtime and maximizing output.
- Enhanced decision-making: Real-time data and comprehensive reporting provide valuable insights for informed decision-making, enabling manufacturers to optimize production processes and improve overall performance.
 .
.
Challenges of ERP Implementation for Production Planning:
- Data migration and integration: Migrating existing production data and integrating ERP software with legacy systems can be complex and time-consuming.
- Training and user adoption: Training employees to use ERP software and ensuring user adoption can be a challenge, requiring effective communication and ongoing support.
- Customization and configuration: Configuring ERP software to meet specific production planning needs can be complex and require expertise in system customization.
 .
.
2. Optimizing Inventory Management: Balancing Supply and Demand
Inventory management is a delicate balancing act, requiring manufacturers to maintain sufficient stock to meet customer demand while minimizing holding costs and waste. In the absence of a robust system, inventory management can lead to stockouts, excess inventory, and significant financial losses. This is where ERP software comes into play, providing manufacturers with the tools to optimize inventory levels, reduce costs, and ensure timely delivery of products.
Real-time Inventory Tracking:
ERP software provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, allowing manufacturers to track stock movements, monitor consumption rates, and identify potential shortages. This real-time data enables proactive inventory management, ensuring that the right materials are available at the right time.
Automated Inventory Management:
ERP software automates inventory management tasks, eliminating manual errors and ensuring accuracy. Automated processes like purchase order generation, stock replenishment, and inventory allocation streamline operations and reduce the risk of stockouts or excess inventory.
Demand Forecasting and Planning:
ERP software incorporates advanced demand forecasting tools, enabling manufacturers to predict future demand and adjust inventory levels accordingly. By analyzing historical sales data and market trends, ERP software provides accurate demand forecasts, helping manufacturers optimize inventory levels and avoid stockouts or overstocking.
Inventory Optimization Tools:
ERP software offers a range of inventory optimization tools, including ABC analysis, safety stock calculation, and reorder point determination. These tools help manufacturers identify critical inventory items, set appropriate safety stock levels, and minimize holding costs.
Benefits of ERP for Inventory Management:
- Reduced inventory holding costs: Accurate demand forecasting and inventory optimization tools minimize excess inventory, reducing holding costs and freeing up cash flow.
- Minimized stockouts: Real-time inventory tracking and automated replenishment processes ensure that the right materials are available at the right time, minimizing stockouts and avoiding production delays.
- Improved supply chain visibility: ERP software provides real-time visibility into inventory levels across the entire supply chain, enabling manufacturers to track materials and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Enhanced customer service: Timely delivery of products due to optimized inventory management improves customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Challenges of ERP Implementation for Inventory Management:
- Data accuracy and integrity: Ensuring the accuracy and integrity of inventory data is crucial for effective inventory management. This requires careful data migration and ongoing data validation processes.
- Integration with existing systems: Integrating ERP software with existing inventory management systems can be complex and require specialized expertise.
- Customization and configuration: Configuring ERP software to meet specific inventory management needs, such as setting reorder points and safety stock levels, can be challenging.
3. Enhancing Supply Chain Visibility: A Transparent and Efficient Network
In today’s globalized economy, manufacturing businesses operate within complex supply chains, involving multiple suppliers, distributors, and logistics providers. Maintaining visibility across this intricate network is essential for efficient operations and timely delivery of products. ERP software provides manufacturers with the tools to gain real-time insights into their supply chains, enabling proactive management and minimizing disruptions.
Real-time Supplier Tracking:
ERP software provides real-time visibility into supplier performance, allowing manufacturers to track orders, monitor delivery schedules, and identify potential delays. This information empowers manufacturers to proactively address supply chain issues, ensuring timely delivery of materials and minimizing production disruptions.
Supply Chain Collaboration:
ERP software facilitates collaboration between manufacturers and their suppliers, enabling seamless information sharing and communication. This collaborative environment streamlines processes, reduces communication errors, and improves overall supply chain efficiency.
Demand Planning and Forecasting:
ERP software incorporates demand planning and forecasting tools, enabling manufacturers to anticipate future demand and adjust their supply chains accordingly. By analyzing historical sales data and market trends, ERP software provides accurate demand forecasts, helping manufacturers optimize production and procurement plans to meet anticipated demand.
Logistics and Transportation Management:
ERP software integrates with logistics and transportation management systems, providing real-time visibility into shipment tracking, delivery schedules, and transportation costs. This information enables manufacturers to optimize transportation routes, minimize shipping costs, and ensure timely delivery of products.
Benefits of ERP for Supply Chain Visibility:
- Reduced supply chain disruptions: Real-time visibility into supplier performance and delivery schedules enables manufacturers to proactively address supply chain issues, minimizing disruptions and ensuring timely delivery of materials.
- Improved supply chain efficiency: Collaborative tools and seamless information sharing streamline supply chain processes, reducing communication errors and improving overall efficiency.
- Optimized transportation costs: Real-time shipment tracking and transportation management tools enable manufacturers to optimize routes, minimize shipping costs, and ensure timely delivery of products.
- Enhanced customer service: Timely delivery of products due to a well-managed supply chain improves customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Challenges of ERP Implementation for Supply Chain Visibility:
- Integration with third-party systems: Integrating ERP software with third-party logistics providers and suppliers can be complex and require specialized expertise.
- Data security and privacy: Ensuring the security and privacy of sensitive supply chain data is crucial. This requires robust security measures and compliance with relevant regulations.
- Change management and adoption: Implementing ERP software for supply chain visibility requires significant change management efforts to ensure buy-in from all stakeholders.
4. Enhancing Customer Service: Building Strong Relationships
In today’s competitive landscape, providing exceptional customer service is no longer a luxury but a necessity for business success. ERP software empowers manufacturers to deliver personalized customer experiences, improve communication, and build lasting relationships.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Integration:
ERP software often integrates with CRM systems, providing a comprehensive view of customer interactions, purchase history, and preferences. This integrated data enables manufacturers to personalize customer communications, offer tailored solutions, and provide exceptional service.
Real-time Order Tracking:
ERP software provides real-time order tracking capabilities, allowing customers to monitor the progress of their orders and receive timely updates. This transparency improves communication, builds trust, and enhances customer satisfaction.
Automated Order Processing:
ERP software automates order processing tasks, reducing errors and ensuring timely order fulfillment. Automated processes like order confirmation, invoice generation, and shipping notifications streamline operations and improve customer experience.
Customer Support and Service:
ERP software can be integrated with customer support and service platforms, providing a centralized hub for managing inquiries, resolving issues, and providing assistance. This integrated approach ensures consistent customer service and enhances customer satisfaction.
Benefits of ERP for Customer Service:
- Improved customer satisfaction: Personalized communications, real-time order tracking, and efficient order processing enhance customer experience and build loyalty.
- Enhanced customer relationships: Integrated CRM data enables manufacturers to understand customer needs and preferences, fostering stronger relationships and driving repeat business.
- Increased sales and revenue: Exceptional customer service leads to higher customer satisfaction, increased referrals, and ultimately, higher sales and revenue.
- Reduced customer churn: By addressing customer concerns promptly and providing personalized service, ERP software helps manufacturers retain customers and reduce churn.
Challenges of ERP Implementation for Customer Service:
- Data integration and consistency: Ensuring data consistency between ERP and CRM systems is crucial for providing personalized customer experiences. This requires careful data migration and ongoing data validation processes.
- Customization and configuration: Configuring ERP software to meet specific customer service needs, such as setting up automated communication channels and integrating with customer support platforms, can be challenging.
- User training and adoption: Training employees to use ERP software for customer service and ensuring user adoption can be a challenge, requiring effective communication and ongoing support.
5. Streamlining Financial Management: Gaining Control of Finances
Financial management is a critical aspect of any manufacturing business, requiring accurate tracking of expenses, revenue, and profitability. In the absence of a robust system, financial management can become a complex and error-prone process, leading to inaccurate reporting, missed deadlines, and financial losses. ERP software provides manufacturers with the tools to streamline financial operations, gain real-time visibility into financial performance, and make informed decisions.
Financial Reporting and Analytics:
ERP software provides comprehensive financial reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing manufacturers to track expenses, revenue, and profitability in real-time. This data enables manufacturers to identify trends, analyze performance, and make informed decisions about resource allocation and investment.
Automated Accounting Processes:
ERP software automates accounting processes, reducing manual errors and ensuring accuracy. Automated processes like invoice generation, expense tracking, and bank reconciliation streamline operations and free up valuable time for financial professionals.
Budgeting and Forecasting:
ERP software incorporates budgeting and forecasting tools, enabling manufacturers to plan for future expenses and revenue. By analyzing historical data and market trends, ERP software provides accurate financial forecasts, helping manufacturers make informed decisions about resource allocation and investment.
Financial Compliance and Audit:
ERP software helps manufacturers comply with financial regulations and streamline audit processes. Automated reporting and data tracking ensure accurate recordkeeping, simplifying audits and reducing the risk of non-compliance.
Benefits of ERP for Financial Management:
- Improved financial accuracy: Automated accounting processes and real-time data tracking reduce errors and ensure accurate financial reporting.
- Enhanced financial visibility: Comprehensive financial reporting and analytics provide real-time insights into financial performance, enabling manufacturers to identify trends and make informed decisions.
- Streamlined financial operations: Automated processes and integrated systems streamline financial operations, freeing up valuable time for financial professionals to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Improved financial compliance: Automated reporting and data tracking ensure accurate recordkeeping, simplifying audits and reducing the risk of non-compliance.
Challenges of ERP Implementation for Financial Management:
- Data migration and integration: Migrating existing financial data and integrating ERP software with legacy accounting systems can be complex and time-consuming.
- Customization and configuration: Configuring ERP software to meet specific financial management needs, such as setting up custom reports and integrating with financial institutions, can be challenging.
- User training and adoption: Training employees to use ERP software for financial management and ensuring user adoption can be a challenge, requiring effective communication and ongoing support.
6. Optimizing Human Resources Management: Engaging and Empowering Employees
In today’s competitive job market, attracting and retaining top talent is crucial for manufacturing businesses. ERP software provides manufacturers with the tools to manage human resources effectively, engage employees, and foster a positive work environment.
Talent Acquisition and Management:
ERP software integrates with talent acquisition platforms, streamlining the recruitment process and enabling manufacturers to attract and hire top talent. Automated tasks like job posting, candidate screening, and interview scheduling save time and improve efficiency.
Employee Performance Management:
ERP software provides tools for performance management, enabling manufacturers to set goals, track progress, and provide feedback to employees. Automated performance reviews and goal-setting processes ensure consistent evaluation and facilitate employee development.
Payroll and Benefits Administration:
ERP software streamlines payroll and benefits administration, automating tasks like time tracking, payroll processing, and benefits enrollment. This automation reduces errors, ensures timely payments, and improves employee satisfaction.
Employee Training and Development:
ERP software can be integrated with learning management systems, providing a platform for employee training and development. This allows manufacturers to deliver online courses, track progress, and ensure that employees have the skills and knowledge they need to succeed.
Benefits of ERP for Human Resources Management:
- Improved employee engagement: Streamlined processes, automated tasks, and access to relevant information empower employees and enhance their job satisfaction.
- Enhanced talent acquisition: Integrated talent acquisition platforms streamline the recruitment process, enabling manufacturers to attract and hire top talent.
- Effective performance management: Performance management tools enable manufacturers to set goals, track progress, and provide feedback to employees, fostering growth and development.
- Streamlined payroll and benefits administration: Automated processes ensure timely payments, reduce errors, and improve employee satisfaction.
Challenges of ERP Implementation for Human Resources Management:
- Data security and privacy: Ensuring the security and privacy of sensitive employee data is crucial. This requires robust security measures and compliance with relevant regulations.
- Integration with existing systems: Integrating ERP software with existing HR systems can be complex and require specialized expertise.
- Change management and adoption: Implementing ERP software for HR management requires significant change management efforts to ensure buy-in from employees and managers.
7. Enhancing Quality Control: Ensuring Excellence in Every Product
Quality control is paramount in manufacturing, ensuring that every product meets the highest standards and satisfies customer expectations. ERP software provides manufacturers with the tools to track quality metrics, identify potential issues, and implement corrective actions, ultimately improving product quality and reducing defects.
Quality Management System (QMS) Integration:
ERP software often integrates with QMS systems, providing a centralized platform for managing quality control processes. This integration enables manufacturers to track quality metrics, identify potential issues, and implement corrective actions.
Automated Quality Inspections:
ERP software can automate quality inspections, reducing manual errors and ensuring consistent quality standards. Automated processes like inspection scheduling, data collection, and defect reporting streamline operations and improve efficiency.
Non-Conformance Tracking and Reporting:
ERP software provides tools for tracking non-conformances, identifying root causes, and implementing corrective actions. This data enables manufacturers to identify areas for improvement and reduce the risk of future defects.
Quality Data Analysis and Reporting:
ERP software provides comprehensive quality data analysis and reporting capabilities, enabling manufacturers to track quality metrics, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions about process improvements.
Benefits of ERP for Quality Control:
- Improved product quality: Automated inspections, non-conformance tracking, and data analysis help manufacturers identify and address quality issues, leading to higher-quality products.
- Reduced defects and rework: By identifying and addressing potential issues early, ERP software helps manufacturers reduce defects and minimize rework, saving time and money.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction: Higher-quality products and reduced defects lead to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Improved operational efficiency: Streamlined quality control processes and automated tasks improve operational efficiency, reducing downtime and maximizing output.
Challenges of ERP Implementation for Quality Control:
- Data accuracy and integrity: Ensuring the accuracy and integrity of quality data is crucial for effective quality control. This requires careful data migration and ongoing data validation processes.
- Integration with existing systems: Integrating ERP software with existing QMS systems can be complex and require specialized expertise.
- User training and adoption: Training employees to use ERP software for quality control and ensuring user adoption can be a challenge, requiring effective communication and ongoing support.
8. Enhancing Reporting and Analytics: Gaining Insights for Strategic Decisions
Data is the lifeblood of any manufacturing business, providing valuable insights into performance, trends, and opportunities. ERP software provides manufacturers with comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities, enabling them to make data-driven decisions and optimize operations.
Real-time Dashboards and Reports:
ERP software provides real-time dashboards and reports, giving manufacturers a comprehensive view of key performance indicators (KPIs) across various departments and functions. This data enables manufacturers to monitor progress, identify trends, and make informed decisions.
Customizable Reports and Analytics:
ERP software allows manufacturers to create customized reports and analytics, tailoring the data to their specific needs and business objectives. This flexibility enables manufacturers to gain deeper insights into specific areas of interest and make data-driven decisions.
Predictive Analytics and Forecasting:
ERP software incorporates predictive analytics and forecasting tools, enabling manufacturers to anticipate future trends and make proactive decisions. By analyzing historical data and market trends, ERP software provides accurate forecasts, helping manufacturers optimize operations and plan for future growth.
Benefits of ERP for Reporting and Analytics:
- Improved decision-making: Real-time data and comprehensive reporting provide valuable insights for informed decision-making, enabling manufacturers to optimize operations and improve overall performance.
- Enhanced visibility and transparency: Real-time dashboards and reports provide a clear and comprehensive view of key performance indicators, fostering transparency and accountability across the organization.
- Proactive problem-solving: Predictive analytics and forecasting tools enable manufacturers to anticipate potential issues and take proactive steps to mitigate risks.
- Data-driven optimization: Data-driven insights enable manufacturers to identify areas for improvement, optimize processes, and enhance overall efficiency.
Challenges of ERP Implementation for Reporting and Analytics:
- Data quality and integrity: Ensuring the accuracy and integrity of data is crucial for generating reliable reports and analytics. This requires careful data migration and ongoing data validation processes.
- Data security and privacy: Ensuring the security and privacy of sensitive business data is paramount. This requires robust security measures and compliance with relevant regulations.
- User training and adoption: Training employees to use ERP software for reporting and analytics and ensuring user adoption can be a challenge, requiring effective communication and ongoing support.
9. Choosing the Right ERP Software: A Strategic Decision
Choosing the right ERP software is a critical decision for any manufacturing business, as it will impact the efficiency, profitability, and long-term success of the organization. The selection process requires careful consideration of several factors, including business needs, budget, and implementation challenges.
Identify Business Needs:
The first step in choosing ERP software is to identify the specific business needs that the software should address. This involves analyzing current processes, identifying pain points, and defining desired outcomes. For manufacturers, key considerations include production planning, inventory management, supply chain visibility, customer service, financial management, human resources, and quality control.
Evaluate Software Features and Functionality:
Once you have identified your business needs, you need to evaluate the features and functionality of different ERP software solutions. Consider factors like industry-specific modules, integration capabilities, reporting and analytics tools, user interface, and mobile accessibility.
Assess Budget and Implementation Costs:
ERP software comes with a range of pricing models, from subscription-based to perpetual licenses. It’s essential to assess your budget and consider the implementation costs, including software licensing, customization, training, and ongoing support.
Consider Implementation Challenges:
Implementing ERP software can be a complex process, requiring careful planning, data migration, integration with existing systems, and user training. It’s important to consider the potential implementation challenges and ensure that you have the resources and expertise to successfully implement the software.
Benefits of Choosing the Right ERP Software:
- Improved efficiency and productivity: The right ERP software can streamline operations, automate tasks, and reduce manual errors, leading to improved efficiency and productivity.
- Enhanced profitability: By optimizing processes, reducing costs, and improving decision-making, ERP software can contribute to increased profitability.
- Increased customer satisfaction: ERP software can help manufacturers provide better customer service, improve product quality, and deliver products on time, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
- Competitive advantage: Implementing ERP software can give manufacturers a competitive advantage by enabling them to operate more efficiently, respond to market changes quickly, and deliver innovative products and services.
Challenges of Choosing the Right ERP Software:
- Overwhelming options: The market for ERP software is vast and complex, with a wide range of solutions available. Choosing the right software can be overwhelming, requiring careful research and evaluation.
- Implementation complexity: Implementing ERP software can be a complex process, requiring significant time, resources, and expertise.
- Cost and budget constraints: ERP software can be expensive, and implementation costs can add up quickly. It’s important to assess your budget and consider the long-term costs of ownership.
10. Implementing ERP Software: A Strategic Approach
Implementing ERP software is a significant undertaking, requiring careful planning, execution, and ongoing support. A well-defined implementation strategy is essential for ensuring a successful transition and maximizing the benefits of the new software.
Define Project Scope and Objectives:
The first step in ERP implementation is to define the project scope and objectives. This involves identifying the specific processes and departments that will be impacted by the software, defining the desired outcomes, and setting realistic timelines.
Data Migration and Integration:
Migrating existing data and integrating ERP software with legacy systems is a critical step in implementation. This requires careful planning, data cleansing, and testing to ensure data accuracy and integrity.
User Training and Adoption:
Training employees to use ERP software and ensuring user adoption is crucial for successful implementation. This requires effective communication, hands-on training, and ongoing support to address user questions and concerns.
Change Management and Communication:
Implementing ERP software involves significant change management efforts, requiring clear communication and stakeholder engagement. It’s important to address employee concerns, provide training and support, and celebrate successes along the way.
Testing and Go-Live:
Before going live with the new software, it’s essential to conduct thorough testing to ensure that the system is functioning as expected and meets all business requirements. This involves user acceptance testing, system integration testing, and performance testing.
Benefits of Successful ERP Implementation:
- Improved efficiency and productivity: A well-implemented ERP system can streamline operations, automate tasks, and reduce manual errors, leading to improved efficiency and productivity.
- Enhanced profitability: By optimizing processes, reducing costs, and improving decision-making, ERP software can contribute to increased profitability.
- Increased customer satisfaction: ERP software can help manufacturers provide better customer service, improve product quality, and deliver products on time, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
- Competitive advantage: Implementing ERP software can give manufacturers a competitive advantage by enabling them to operate more efficiently, respond to market changes quickly, and deliver innovative products and services.
Challenges of ERP Implementation:
- Resistance to change: Employees may resist the implementation of new software, fearing job losses or changes in their work routines.
- Data migration and integration: Migrating existing data and integrating ERP software with legacy systems can be complex and time-consuming.
- User training and adoption: Training employees to use ERP software and ensuring user adoption can be a challenge, requiring effective communication and ongoing support.
- Cost overruns and delays: ERP implementation projects can be prone to cost overruns and delays if not properly planned and managed.
11. Maintaining and Optimizing ERP Software: A Continuous Journey
Implementing ERP software is not a one-time event but an ongoing process that requires ongoing maintenance, optimization, and adaptation to meet evolving business needs.
Regular Software Updates and Patches:
Software vendors release regular updates and patches to address security vulnerabilities, improve performance, and add new features. It’s essential to install these updates promptly to ensure that the ERP software is secure, reliable, and up-to-date.
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery:
Regular data backups and disaster recovery plans are crucial for protecting business data and ensuring business continuity in case of system failures or data loss.
User Training and Support:
Ongoing user training and support are essential for ensuring that employees are comfortable using the ERP software and can leverage its full capabilities.
Process Improvement and Optimization:
As your business evolves, you may need to adjust your ERP system to accommodate new processes, workflows, or reporting requirements. This requires ongoing analysis, process improvement initiatives, and system configuration changes.
Benefits of Maintaining and Optimizing ERP Software:
- Improved system performance: Regular updates and patches ensure that the ERP software is secure, reliable, and up-to-date, improving system performance and reducing downtime.
- Enhanced data security: Data backup and disaster recovery plans protect business data and ensure business continuity in case of system failures or data loss.
- Increased user adoption: Ongoing user training and support ensure that employees are comfortable using the ERP software and can leverage its full capabilities.
- Improved business processes: Process improvement and optimization initiatives ensure that the ERP system is aligned with evolving business needs, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
Challenges of Maintaining and Optimizing ERP Software:
- Cost of updates and maintenance: Software updates, patches, and maintenance can be expensive, requiring ongoing budget allocation.
- Resource constraints: Maintaining and optimizing ERP software requires dedicated resources, including IT personnel, system administrators, and trainers.
- Resistance to change: Employees may resist changes to the ERP system, fearing disruptions to their work routines or loss of familiarity with the software.
12. The Future of ERP Software: Trends and Innovations
The landscape of ERP software is constantly evolving, with new trends and innovations emerging to meet the changing needs of businesses.
Cloud-Based ERP Solutions:
Cloud-based ERP solutions are gaining popularity, offering several advantages over traditional on-premise systems, including scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
AI and ML are transforming ERP software, enabling predictive analytics, automated decision-making, and personalized user experiences.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration:
ERP software is increasingly integrating with IoT devices, enabling real-time data collection, process automation, and predictive maintenance.
Benefits of the Future of ERP Software:
- Enhanced efficiency and productivity: Cloud-based solutions, AI, and ML enable manufacturers to automate tasks, optimize processes, and make data-driven decisions, leading to improved efficiency and productivity.
- Improved scalability and flexibility: Cloud-based ERP solutions offer greater scalability and flexibility, allowing manufacturers to adapt to changing business needs and market conditions.
- Enhanced decision-making: AI and ML provide predictive analytics and automated insights, empowering manufacturers to make more informed decisions.
- Increased innovation: The integration of IoT devices and AI enables manufacturers to develop new products and services, innovate their business models, and gain a competitive advantage.
Challenges of the Future of ERP Software:
- Security concerns: Cloud-based ERP solutions raise concerns about data security and privacy, requiring robust security measures and compliance with relevant regulations.
- Integration complexity: Integrating ERP software with other systems, such as CRM, QMS, and IoT devices, can be complex and require specialized expertise.
- Change management: Implementing new ERP features and technologies requires significant change management efforts to ensure user adoption and minimize disruptions to business operations.
13. ERP Software for Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Summary
ERP software is a powerful tool that can transform manufacturing businesses, streamlining operations, enhancing efficiency, and driving profitability. By integrating various departments and functions, ERP software provides real-time visibility into business performance, enabling data-driven decision-making and process optimization.
Key Features of ERP Software for Manufacturing:
- Production Planning: Streamlines production schedules, optimizes resource allocation, and automates material requirements planning.
- Inventory Management: Provides real-time inventory tracking, automates replenishment processes, and incorporates demand forecasting tools.
- Supply Chain Visibility: Enables real-time supplier tracking, facilitates collaboration, and optimizes transportation costs.
- Customer Service: Integrates with CRM systems, provides real-time order tracking, and automates order processing.
- Financial Management: Provides comprehensive financial reporting, automates accounting processes, and incorporates budgeting and forecasting tools.
- Human Resources Management: Streamlines talent acquisition, enables performance management, and automates payroll and benefits administration.
- Quality Control: Integrates with QMS systems, automates quality inspections, and provides tools for non-conformance tracking and reporting.
- Reporting and Analytics: Provides real-time dashboards and reports, enables customizable analytics, and incorporates predictive forecasting tools.
Benefits of ERP Software for Manufacturing:
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity: Streamlines operations, automates tasks, and reduces manual errors, leading to improved efficiency and productivity.
- Enhanced Profitability: Optimizes processes, reduces costs, and improves decision-making, contributing to increased profitability.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Provides better customer service, improves product quality, and delivers products on time, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
- Competitive Advantage: Enables manufacturers to operate more efficiently, respond to market changes quickly, and deliver innovative products and services, giving them a competitive advantage.
Challenges of ERP Implementation:
- Choosing the Right Software: Requires careful consideration of business needs, budget, and implementation challenges.
- Implementation Complexity: Involves data migration, integration with existing systems, and user training.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist the implementation of new software, fearing job losses or changes in their work routines.
- Cost Overruns and Delays: ERP implementation projects can be prone to cost overruns and delays if not properly planned and managed.
Maintaining and Optimizing ERP Software:
- Regular Software Updates and Patches: Ensures that the ERP software is secure, reliable, and up-to-date.
- Data Backup and Disaster Recovery: Protects business data and ensures business continuity in case of system failures or data loss.
- User Training and Support: Ensures that employees are comfortable using the ERP software and can leverage its full capabilities.
- Process Improvement and Optimization: Ensures that the ERP system is aligned with evolving business needs, enhancing efficiency and productivity.
The Future of ERP Software:
- Cloud-Based ERP Solutions: Offer scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): Enable predictive analytics, automated decision-making, and personalized user experiences.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: Enables real-time data collection, process automation, and predictive maintenance.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of ERP Software for Manufacturing Success
In the dynamic world of manufacturing, where efficiency and profitability are paramount, ERP software stands as a transformative force, empowering businesses to unlock their full potential. By integrating various departments and functions, ERP software provides real-time visibility into operations, enabling data-driven decision-making, process optimization, and ultimately, sustainable growth.
The journey to ERP implementation is not without its challenges, but the rewards are substantial. By carefully considering business needs, choosing the right software, and implementing it strategically, manufacturers can reap the benefits of improved efficiency, enhanced profitability, and increased customer satisfaction.
As you embark on your ERP journey, remember that it’s not just about implementing the software but about embracing the change it brings. Empower your employees, foster collaboration, and leverage the power of data to drive innovation and achieve lasting success.
Disclaimer: This article is intended to provide general information about ERP software for manufacturing and should not be considered professional advice. It is essential to consult with industry experts and software vendors to determine the best ERP solution for your specific business needs.
 .
.

