The Art and Science of Software Distribution: A Comprehensive Guide for Success
 .
.
Welcome, fellow software enthusiasts! In today’s digital landscape, where innovation reigns supreme and technology constantly evolves, the ability to effectively distribute software is paramount to achieving success. It’s not just about creating a stellar product; it’s about ensuring that your creation reaches its intended audience, resonates with their needs, and ultimately drives adoption.
Software distribution, in its essence, is the process of making your software accessible to users. It encompasses a multitude of strategies, from traditional methods like physical media to modern approaches like online marketplaces and cloud-based platforms. The journey of software distribution is multifaceted, intertwining with various aspects of marketing, sales, customer support, and technical infrastructure.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of software distribution, providing you with a roadmap to navigate the complexities and unlock the potential of your software. We’ll explore the various distribution channels, dissect the advantages and disadvantages of each, and equip you with the knowledge and tools to make informed decisions.
From understanding your target audience and crafting compelling marketing campaigns to optimizing your software for seamless user experience and building a robust support system, we’ll cover it all. By the end of this journey, you’ll be armed with the insights and strategies to effectively distribute your software, maximize its reach, and propel your business forward.
 .
.
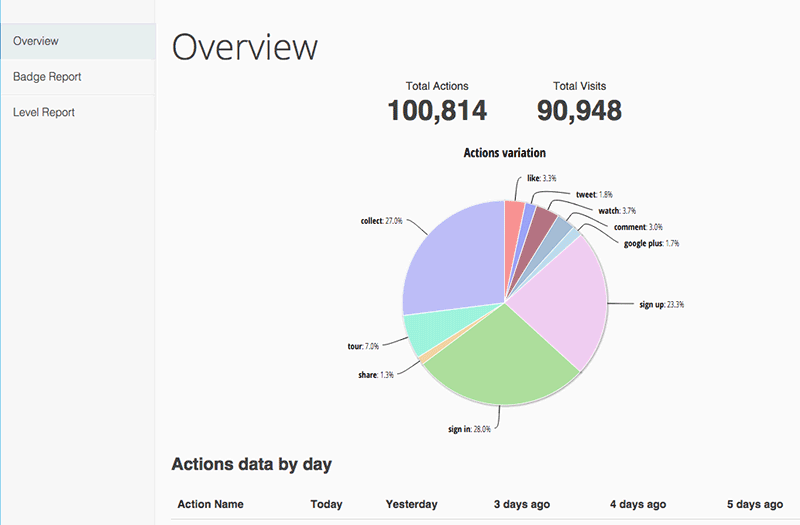
Understanding the Landscape: A Glimpse into Software Distribution Channels
The world of software distribution is a dynamic ecosystem, offering a diverse array of channels for reaching your target audience. Each channel possesses its unique strengths and weaknesses, catering to specific user preferences and market segments.
Direct Downloads: This classic approach allows users to download your software directly from your website. It grants you complete control over the distribution process, enabling you to personalize the experience and collect valuable user data. However, it requires significant effort in marketing and promoting your software to drive downloads.
Online Marketplaces: Platforms like the Apple App Store, Google Play Store, and Steam provide a centralized hub for software distribution, offering a vast user base and established payment infrastructure. While these platforms simplify the distribution process, they often come with stringent guidelines and fees, potentially limiting your control over pricing and marketing.
Software as a Service (SaaS): This subscription-based model delivers your software over the internet, eliminating the need for downloads and installations. SaaS offers flexibility, scalability, and continuous updates, but it requires a robust cloud infrastructure and ongoing maintenance.
Physical Media: Although less common in the digital age, physical media like CDs and DVDs can still be effective for distributing software, especially for niche markets or specific use cases. It offers a tangible experience and can be bundled with other marketing materials.
 .
.
Partnerships and Resellers: Collaborating with other companies to distribute your software can expand your reach and tap into new markets. However, it requires careful selection of partners and negotiation of favorable terms.
Open Source Distribution: This model encourages collaboration and community involvement by making your software’s source code freely available. It fosters innovation and can attract a dedicated user base, but it requires a strong commitment to community engagement and ongoing support.
Navigating the Advantages and Disadvantages of Software Distribution
As with any business strategy, software distribution comes with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. It’s crucial to weigh these factors carefully to make informed decisions that align with your business goals and target audience.
Advantages of Software Distribution:
 .
.
- Increased Reach: Reaching a wider audience through various distribution channels expands your customer base and maximizes your software’s potential impact.
- Revenue Generation: Software distribution monetizes your creation, allowing you to generate revenue and sustain your business.
- Brand Building: Effective distribution strategies enhance your brand visibility, build trust with users, and establish your software as a valuable solution.
- User Feedback and Iteration: Distribution channels provide valuable feedback from users, enabling you to refine your software and improve its functionality.
- Competitive Advantage: Distributing your software strategically gives you a competitive edge in the market, attracting new customers and retaining existing ones.
 .
.
Disadvantages of Software Distribution:
- Competition: The software market is highly competitive, demanding aggressive marketing and continuous innovation to stand out.
- Cost and Resources: Developing and maintaining a robust distribution strategy requires significant financial and human resources.
- Technical Challenges: Ensuring seamless software delivery and addressing technical issues requires expertise and ongoing maintenance.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Software distribution must comply with various legal and regulatory frameworks, adding complexity to the process.
- User Acquisition Costs: Attracting new users and driving adoption can be expensive, requiring targeted marketing campaigns and effective user acquisition strategies.
 .
.
Essential Elements of a Successful Software Distribution Strategy
A well-defined software distribution strategy is the foundation for success. It’s not just about choosing the right channels; it’s about aligning your approach with your target audience, business goals, and market dynamics. Here are the key elements to consider:
1. Define Your Target Audience:
- Who are your ideal users? Understanding their demographics, needs, and preferences is crucial for tailoring your distribution strategy.
- What are their pain points? Identify the problems your software solves and position it as the solution they’ve been seeking.
- Where do they spend their time online? Determine the platforms and channels they frequent to maximize your marketing efforts.
2. Choose the Right Distribution Channels:
- Consider your target audience’s preferences. Select channels that align with their online behavior and technology adoption.
- Evaluate the cost and resources required for each channel. Balance your budget with the potential return on investment.
- Assess the competition in each channel. Choose channels where you can differentiate yourself and stand out from the crowd.
3. Optimize Your Software for Distribution:
- Ensure compatibility and performance across different platforms and devices. Test your software thoroughly for seamless user experience.
- Provide clear and concise installation instructions. Make it easy for users to download, install, and use your software.
- Offer multiple language options. Expand your reach to a global audience by supporting diverse languages.
4. Develop a Compelling Marketing Strategy:
- Create a strong brand identity and messaging. Communicate the value proposition of your software clearly and persuasively.
- Utilize a mix of marketing channels, including social media, email marketing, content marketing, and paid advertising. Reach your target audience where they are.
- Track your marketing campaign performance and make adjustments as needed. Optimize your strategies for maximum impact.
5. Provide Excellent Customer Support:
- Offer comprehensive documentation and FAQs. Empower users to resolve common issues independently.
- Provide responsive and helpful customer support channels. Address user concerns promptly and effectively.
- Collect feedback from users to improve your software and customer support experience. Continuously strive for excellence.
6. Build a Strong Community:
- Engage with users on social media and online forums. Foster a sense of community and build relationships with your customers.
- Offer exclusive content and resources to your community members. Reward their loyalty and encourage continued engagement.
- Host events and webinars to connect with users and showcase your software’s capabilities. Create opportunities for interaction and feedback.
7. Embrace Continuous Improvement:
- Monitor your distribution strategy’s performance and make adjustments as needed. Adapt to changing market dynamics and user preferences.
- Stay informed about emerging technologies and trends. Explore new distribution channels and innovative approaches.
- Continuously refine your software and customer support experience. Strive for excellence and delight your users.
FAQs: Addressing Common Software Distribution Questions
1. What are the most effective ways to promote my software?
- Content marketing: Create valuable content that resonates with your target audience, showcasing the benefits of your software.
- Social media marketing: Engage with your target audience on relevant platforms, sharing updates and building a community.
- Email marketing: Build an email list and send targeted campaigns to nurture leads and promote your software.
- Paid advertising: Utilize platforms like Google Ads and Facebook Ads to reach a wider audience and drive traffic to your website.
2. How do I choose the right pricing model for my software?
- Free trial: Offer a limited-time free trial to allow users to experience your software before committing to a purchase.
- Subscription-based: Charge a recurring fee for access to your software, providing ongoing value and revenue streams.
- One-time purchase: Offer a single payment for lifetime access to your software, suitable for niche markets or specific use cases.
- Freemium model: Provide a free basic version of your software with limited features, offering premium features for a fee.
3. How can I ensure my software is secure and reliable?
- Implement robust security measures: Protect user data and prevent unauthorized access to your software.
- Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability testing. Identify and address potential security risks.
- Provide regular updates and patches: Fix bugs, address security vulnerabilities, and improve software performance.
4. What are the best practices for managing software updates?
- Communicate update schedules and release notes clearly. Inform users about upcoming updates and their impact.
- Offer automatic updates for seamless user experience. Allow users to update their software without manual intervention.
- Provide rollback options in case of update issues. Enable users to revert to previous versions if necessary.
5. How can I measure the success of my software distribution strategy?
- Track key metrics: Monitor downloads, installations, user engagement, customer satisfaction, and revenue generated.
- Analyze user feedback: Gather insights from user reviews, surveys, and support tickets to identify areas for improvement.
- Compare your performance to industry benchmarks. Assess your progress against competitors and industry standards.
6. What are the legal considerations for software distribution?
- Copyright and intellectual property: Protect your software with copyright and other intellectual property rights.
- Privacy and data protection: Comply with data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
- Software licensing agreements: Establish clear terms and conditions for software usage and distribution.
7. How can I leverage data analytics to improve my software distribution?
- Track user behavior: Analyze user interactions with your software to understand their preferences and needs.
- Identify trends and patterns: Discover emerging trends and user segments to optimize your marketing efforts.
- Personalize user experiences: Tailor your software and marketing messages based on user data.
8. What are the best tools for software distribution?
- Online marketplaces: Platforms like the App Store, Google Play Store, and Steam offer a centralized distribution hub.
- Cloud-based platforms: Services like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud provide infrastructure for hosting and distributing software.
- Software distribution platforms: Tools like ClickOnce, InstallShield, and Advanced Installer simplify the distribution process.
- Marketing automation tools: Platforms like Mailchimp, HubSpot, and Marketo streamline email marketing and lead generation.
9. How can I build a successful software distribution team?
- Hire individuals with expertise in software distribution, marketing, customer support, and technical infrastructure.
- Foster a collaborative and innovative culture. Encourage teamwork and knowledge sharing.
- Provide ongoing training and development opportunities. Keep your team up-to-date with industry trends and best practices.
10. What are the future trends in software distribution?
- Cloud-native distribution: Software will increasingly be delivered and accessed through the cloud.
- AI-powered distribution: Artificial intelligence will play a greater role in optimizing distribution strategies and personalizing user experiences.
- Emerging technologies: New technologies like blockchain and edge computing will revolutionize software distribution models.
11. How can I overcome the challenges of software distribution?
- Stay informed about industry trends and best practices. Continuously adapt your strategy to changing market dynamics.
- Build strong relationships with partners and customers. Collaborate to expand your reach and build trust.
- Invest in your software’s development and marketing. Allocate resources to ensure your software remains competitive and appealing to users.
12. What are some examples of successful software distribution strategies?
- Slack: Leveraged a freemium model, offering a free basic version and premium features for a fee.
- Zoom: Utilized a combination of direct downloads, online marketplaces, and partnerships to achieve widespread adoption.
- Spotify: Built a successful subscription-based model, offering a vast library of music and personalized recommendations.
13. What are the key takeaways for effective software distribution?
- Define your target audience and their needs.
- Choose the right distribution channels.
- Optimize your software for seamless user experience.
- Develop a compelling marketing strategy.
- Provide excellent customer support.
- Build a strong community.
- Embrace continuous improvement.
Conclusion: Embark on Your Journey to Software Distribution Success
Software distribution is a dynamic and ever-evolving field, demanding a strategic approach to achieve success. By understanding the complexities of distribution channels, leveraging the advantages, and mitigating the disadvantages, you can position your software for maximum reach and impact.
This comprehensive guide has provided you with the knowledge and tools to navigate the intricacies of software distribution. From defining your target audience and choosing the right channels to optimizing your software for user experience and building a strong community, you have a roadmap for success.
Remember, software distribution is not a one-size-fits-all approach. It requires continuous adaptation, experimentation, and a commitment to excellence. Embrace the challenges, learn from your experiences, and never stop striving for improvement.
With a well-defined strategy, a passion for your creation, and a dedication to your users, you can achieve remarkable success in the world of software distribution.
Disclaimer: This article provides general information and insights into software distribution. It is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice. Specific strategies and tactics may vary depending on your software, target audience, and business goals. It is recommended to consult with experts in software distribution, marketing, and legal matters to develop a tailored approach that aligns with your unique circumstances.
 .
.

