Navigating the Labyrinth of ERP Implementation Strategies: A Comprehensive Guide
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems are the backbone of modern business operations, orchestrating a symphony of processes across departments to streamline workflows and enhance efficiency. However, embarking on an ERP implementation journey is akin to traversing a labyrinth, fraught with potential pitfalls and complexities. To navigate this intricate landscape successfully, it is imperative to equip yourself with a comprehensive understanding of ERP implementation strategies, their advantages, disadvantages, and the key considerations for selecting the most suitable approach for your organization.
ERP Implementation Strategies: A Landscape of Options
ERP implementation strategies vary in their scope, complexity, and timelines, catering to the unique needs and circumstances of different organizations. The most common strategies include:
-
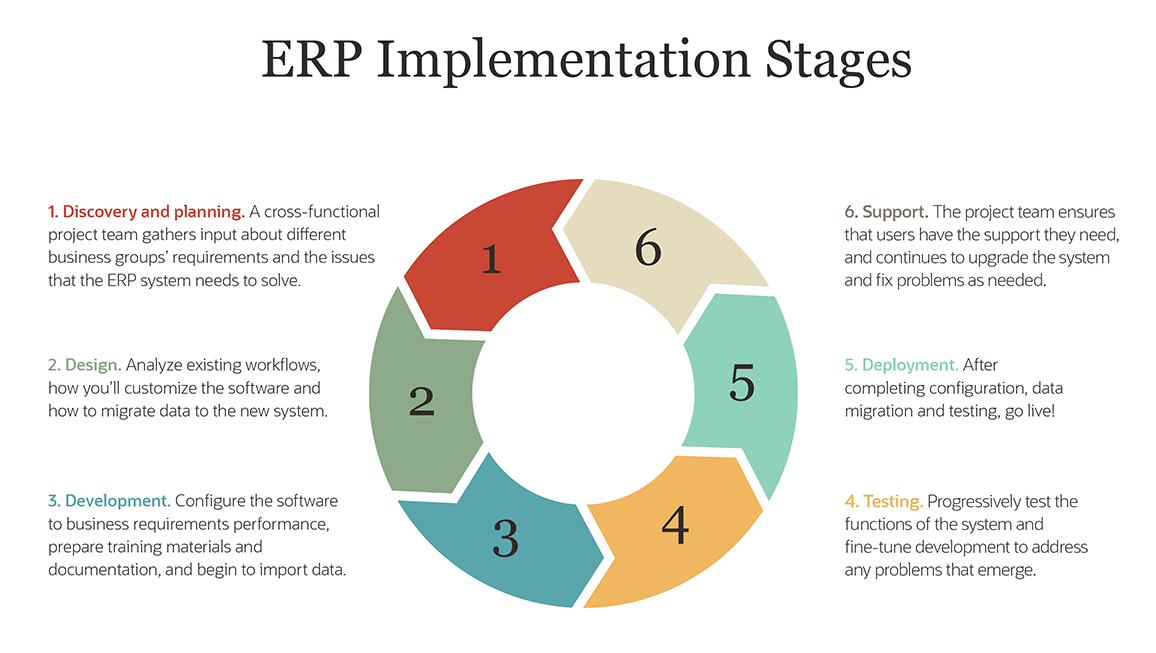
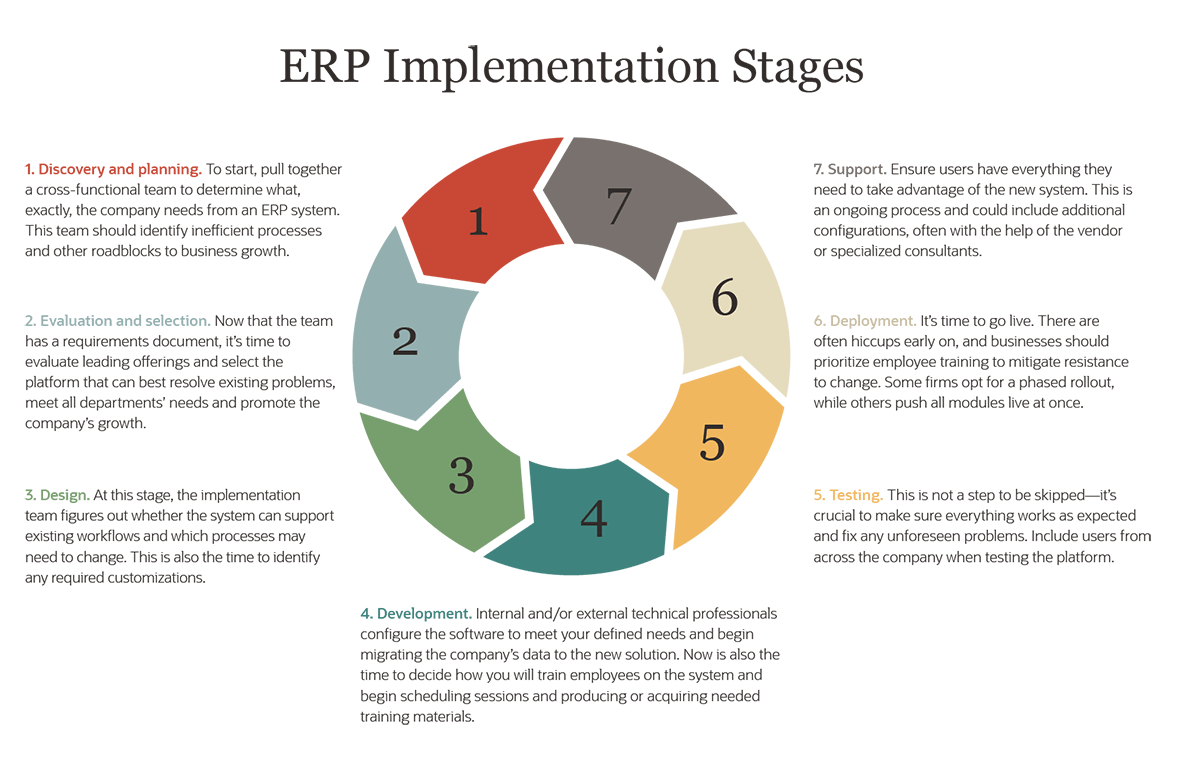
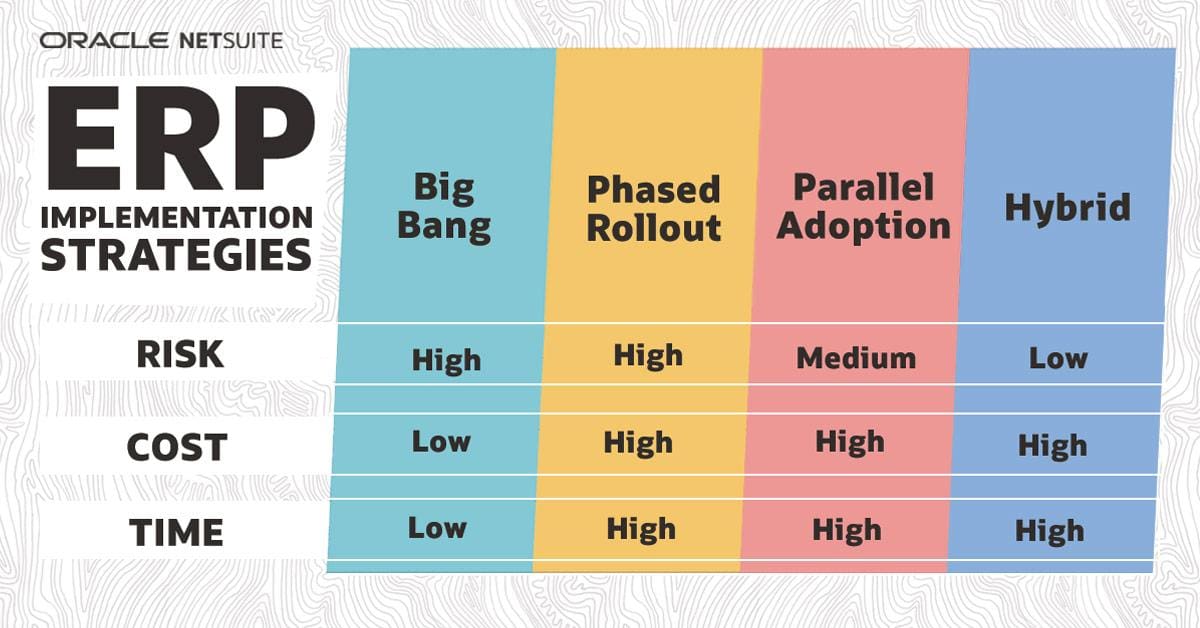
Big Bang Implementation: A bold and decisive approach where the entire ERP system is implemented at once, replacing all existing systems.
-
Phased Implementation: A gradual and methodical approach where the ERP system is implemented in stages, allowing for a smoother transition and less disruption.
-
Parallel Implementation: A cautious approach where the new ERP system runs alongside the existing systems until the transition is complete.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Weighing the Scales
Each ERP implementation strategy carries its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for making an informed decision.
Big Bang Implementation:
-
Advantages:
- Quick and efficient implementation.
- Minimal disruption during the transition.
- Reduced training costs.
-
Disadvantages:
- High risk of failure due to the complexity of the change.
- Potential for significant business disruption.
- Limited flexibility for customization.
Phased Implementation:
-
Advantages:
- Lower risk of failure due to the gradual approach.
- Reduced business disruption.
- Flexibility for customization and adjustments.
-
Disadvantages:
- Longer implementation timeline.
- Potential for higher training costs.
- Risk of delays or setbacks during the transition.
Parallel Implementation:
-
Advantages:
- Minimal business disruption.
- Allows for thorough testing and validation.
- Provides a safety net in case of any issues with the new system.
-
Disadvantages:
- Longer implementation timeline.
- Higher costs due to maintaining two systems.
- Potential for data inconsistencies between systems.
Key Considerations: Charting the Course
Selecting the most appropriate ERP implementation strategy requires careful consideration of several key factors:
-
Organization Size and Complexity: Larger and more complex organizations may benefit from a phased or parallel approach, while smaller organizations may find a big bang implementation more feasible.
-
Existing Systems and Processes: Organizations with complex legacy systems may require a phased or parallel approach to minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition.
-
Business Objectives and Timelines: Organizations with urgent business needs may opt for a big bang implementation to expedite the transition, while those with more flexible timelines may prefer a phased or parallel approach.
-
Budget and Resources: Big bang implementations typically require a larger upfront investment and more resources, while phased and parallel implementations may spread the costs over a longer period.
-
Risk Tolerance: Organizations with a low tolerance for risk may prefer a phased or parallel approach to mitigate the potential for disruption and failure.
Embracing the Power of ERP: A Catalyst for Transformation
ERP systems offer a multitude of benefits that can transform business operations, including:
-
Improved Efficiency: Streamlined processes and automated tasks enhance productivity and reduce operational costs.
-
Enhanced Collaboration: Centralized data and seamless communication foster collaboration across departments and improve decision-making.
-
Increased Visibility: Real-time data and comprehensive reporting provide greater visibility into business performance, enabling data-driven decisions.
-
Improved Customer Service: Integrated CRM capabilities enhance customer interactions and streamline support processes.
-
Competitive Advantage: ERP systems provide a technological edge, enabling organizations to adapt quickly to changing market dynamics and gain a competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions: Unraveling the Mysteries
-
What is the best ERP implementation strategy for my organization?
- The optimal strategy depends on factors such as organization size, complexity, existing systems, business objectives, and risk tolerance.
-
How long does an ERP implementation typically take?
- Implementation timelines vary depending on the strategy chosen, the complexity of the organization, and the scope of the project.
-
What is the cost of ERP implementation?
- Costs vary widely based on factors such as the size and complexity of the organization, the ERP vendor, and the implementation strategy.
-
What are the key challenges of ERP implementation?
- Common challenges include data migration, user adoption, process redesign, and change management.
-
How can I ensure a successful ERP implementation?
- Key success factors include thorough planning, stakeholder involvement, effective communication, and ongoing support.
-
What are the benefits of ERP implementation?
- ERP systems enhance efficiency, collaboration, visibility, customer service, and competitive advantage.
-
How do I choose the right ERP vendor?
- Consider factors such as industry expertise, product capabilities, implementation experience, and customer support.
-
What is the role of change management in ERP implementation?
- Change management is crucial for ensuring user adoption, minimizing resistance, and facilitating a smooth transition.
-
How do I measure the success of ERP implementation?
- Key metrics include improved efficiency, increased collaboration, enhanced visibility, and positive user feedback.
-
What are the common mistakes to avoid during ERP implementation?
- Common pitfalls include underestimating the complexity, neglecting user training, and failing to involve key stakeholders.
-
How do I prepare my organization for ERP implementation?
- Preparation involves thorough planning, stakeholder engagement, process mapping, and data cleansing.
-
What are the best practices for ERP implementation?
- Best practices include defining clear goals, involving users in the process, and establishing a dedicated project team.
-
How do I overcome the challenges of ERP implementation?
- Effective strategies for overcoming challenges include proactive risk management, ongoing communication, and flexible change management.
Conclusion: Embarking on the ERP Odyssey
ERP implementation is a transformative journey that requires careful planning, strategic execution, and unwavering commitment. By understanding the various implementation strategies, their advantages and disadvantages, and the key considerations for selection, organizations can navigate the complexities of ERP implementation and harness its transformative power. With a comprehensive understanding of the challenges and best practices, organizations can embark on this odyssey with confidence, maximizing the benefits of ERP and propelling their businesses towards greater success.
Rebuttal: Dispelling Common Misconceptions
Some critics argue that ERP implementations are inherently complex and disruptive, leading to inevitable setbacks and failures. However, this is a misconception. With meticulous planning, stakeholder involvement, and a commitment to best practices, organizations can mitigate risks and ensure a successful ERP implementation. ERP systems are not merely technological tools; they are strategic investments that can revolutionize business operations, driving efficiency, collaboration, and innovation. By embracing a proactive and collaborative approach, organizations can harness the transformative power of ERP and unlock unprecedented opportunities for growth and success.
