ERP vs Accounting Software: A Comprehensive Guide for Businesses
Introduction
In today’s competitive business landscape, organizations are constantly seeking ways to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and accounting software are two powerful tools that can help businesses achieve these goals. However, understanding the differences between these two solutions is crucial to determine which one is the best fit for your organization’s specific needs. This comprehensive guide will delve into the key distinctions between ERP and accounting software, exploring their respective strengths, weaknesses, and suitability for various business scenarios.
ERP vs Accounting Software: A Comparative Analysis
1. Definition and Scope
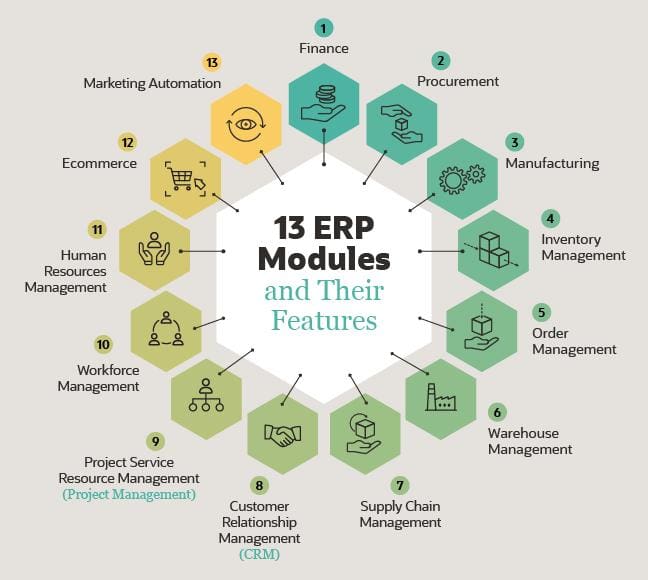
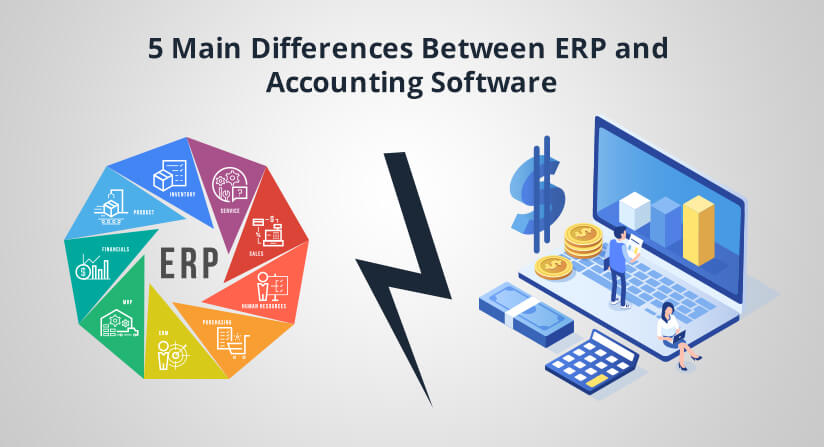
ERP systems are comprehensive software suites that integrate various business functions into a single, centralized platform. They provide a holistic view of an organization’s operations, encompassing modules for finance, accounting, human resources, supply chain management, customer relationship management, and more. In contrast, accounting software is primarily focused on managing financial transactions, including accounts receivable, accounts payable, general ledger, and financial reporting.
2. Integration and Data Management
ERP systems excel in integrating data from multiple departments and systems, creating a single source of truth for business information. This eliminates the need for manual data entry and reduces the risk of errors. Accounting software, on the other hand, is designed to handle financial data specifically and may not offer the same level of integration with other business functions.
3. Customization and Flexibility
ERP systems are highly customizable, allowing businesses to tailor the software to meet their specific requirements. They provide a wide range of modules and features that can be configured to suit different industry verticals and business processes. Accounting software, while typically less customizable than ERP systems, may offer some flexibility in terms of report formats and chart of accounts.
4. Scalability and Growth
ERP systems are designed to support businesses of all sizes, from small start-ups to large enterprises. They can scale to accommodate growing data volumes and increased user requirements. Accounting software, on the other hand, may have limitations in terms of scalability, especially for businesses with complex or high-volume financial operations.
5. Cost and Implementation
ERP systems typically require a significant investment in terms of software licenses, implementation, and ongoing maintenance. Accounting software is generally more affordable and easier to implement, making it a suitable option for small businesses and organizations with limited budgets.
Advantages of ERP Systems
1. Enhanced Data Accuracy and Consistency
ERP systems centralize all business data into a single platform, eliminating data silos and ensuring data accuracy and consistency across the organization. This reduces the risk of errors and improves the reliability of financial reporting.
2. Improved Operational Efficiency
By integrating various business functions, ERP systems streamline workflows, automate tasks, and reduce manual processes. This leads to increased operational efficiency, reduced costs, and improved productivity.
3. Real-Time Visibility and Reporting

ERP systems provide real-time visibility into key business metrics and performance indicators. This enables managers to make informed decisions based on up-to-date information and respond quickly to changing market conditions.
4. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
ERP systems facilitate collaboration and communication between different departments and teams within an organization. By sharing a common platform, employees can access the same information, reducing misunderstandings and improving coordination.
5. Scalability and Growth Potential
ERP systems are designed to support businesses of all sizes and can scale to accommodate growing data volumes and increased user requirements. This makes them a suitable investment for organizations planning for future growth and expansion.
Disadvantages of ERP Systems
1. High Cost and Implementation Complexity
ERP systems require a significant investment in terms of software licenses, implementation, and ongoing maintenance. They can also be complex to implement, requiring specialized expertise and downtime during the transition.
2. Customization Challenges
While ERP systems are customizable, the process of tailoring them to meet specific business requirements can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. Organizations may need to invest in additional development and consulting services to achieve the desired level of customization.
3. Training and Adoption
Implementing an ERP system requires significant training for users to become proficient in the new software. This can be a challenge for organizations with large or geographically dispersed workforces.
4. Potential for Disruption
ERP implementations can be disruptive to business operations, especially during the initial transition phase. Organizations need to carefully plan and manage the implementation process to minimize disruptions and ensure a smooth transition.
5. Ongoing Maintenance and Updates
ERP systems require ongoing maintenance and updates to ensure optimal performance and security. This can be an ongoing cost and resource commitment for organizations.
Advantages of Accounting Software
1. Cost-Effective and Easy to Implement
Accounting software is typically more affordable and easier to implement than ERP systems. This makes it a suitable option for small businesses and organizations with limited budgets.
2. Focus on Financial Management
Accounting software is specifically designed to manage financial transactions, including accounts receivable, accounts payable, general ledger, and financial reporting. It provides robust features and functionality for these core accounting tasks.
3. Improved Financial Accuracy and Control
By automating financial processes and providing real-time visibility into financial data, accounting software helps improve financial accuracy and control. This reduces the risk of errors and fraud.
4. Compliance with Regulations
Accounting software helps businesses comply with various financial regulations and reporting requirements. It provides features for tax calculations, audit trails, and financial statement preparation.
5. Scalability for Small and Medium-Sized Businesses
Accounting software is designed to support small and medium-sized businesses with limited financial complexity. It can scale to accommodate growing data volumes and user requirements within these business segments.
Disadvantages of Accounting Software
1. Limited Integration and Data Sharing
Accounting software is primarily focused on managing financial data and may not offer the same level of integration with other business functions as ERP systems. This can lead to data silos and the need for manual data entry between different systems.
2. Customization Limitations
Accounting software is typically less customizable than ERP systems. Businesses may have limited options to tailor the software to meet their specific requirements and industry-specific needs.
3. Scalability Constraints for Large Enterprises
While accounting software can scale to support small and medium-sized businesses, it may have limitations in terms of scalability for large enterprises with complex financial operations and high-volume data processing requirements.
4. Lack of Advanced Features
Accounting software may lack advanced features and functionality that are available in ERP systems, such as supply chain management, customer relationship management, and human resources management.
5. Limited Real-Time Visibility
Accounting software may not provide real-time visibility into key business metrics and performance indicators beyond financial data. This can limit the ability of managers to make informed decisions based on up-to-date information.
ERP vs Accounting Software: Suitability for Different Business Scenarios
1. Small Businesses with Limited Financial Complexity
For small businesses with limited financial complexity and a need for basic accounting functionality, accounting software is a suitable and cost-effective option.
2. Growing Businesses with Expanding Financial Operations
As businesses grow and their financial operations become more complex, they may outgrow the capabilities of accounting software and require an ERP system to support their expanding needs.
3. Businesses with Complex Supply Chains and Inventory Management
Businesses with complex supply chains and inventory management requirements may benefit from the integrated capabilities of an ERP system, which provides visibility and control over these processes.
4. Organizations with Multiple Business Units and Locations
ERP systems are ideal for organizations with multiple business units and locations, as they provide a centralized platform for managing all operations and ensuring data consistency across the enterprise.
5. Businesses with Industry-Specific Requirements
ERP systems can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of different industries, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and retail. This customization capability makes them a suitable option for businesses operating in these sectors.
Conclusion
ERP and accounting software are both valuable tools for businesses seeking to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. However, understanding the key differences between these two solutions is crucial to determine which one is the best fit for your organization’s specific needs. ERP systems provide a comprehensive suite of integrated modules for various business functions, while accounting software focuses primarily on financial management. Consider the advantages and disadvantages of each solution, as well as your organization’s size, industry, and growth plans, to make an informed decision. By choosing the right solution, you can unlock the full potential of your business and achieve your strategic objectives.
Rebuttal
Some may argue that accounting software is sufficient for all businesses, regardless of size or complexity. While accounting software can provide basic financial management functionality, it may not offer the same level of integration, customization, and scalability as ERP systems. For businesses with complex operations, multiple business units, or industry-specific requirements, an ERP system is often the better choice to support their growth and success.
