ERP Implementation Life Cycle: A Comprehensive Guide to Streamlining Your Business Operations
Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, organizations are constantly seeking ways to optimize their operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have emerged as a powerful tool to achieve these objectives. ERP implementation involves a complex life cycle that encompasses various stages, each with its unique challenges and opportunities. Understanding the intricacies of the ERP implementation life cycle is crucial for businesses to maximize the value of these systems and drive successful outcomes.
1. Planning and Assessment
The initial phase of the ERP implementation life cycle involves meticulous planning and assessment. Organizations must clearly define their business objectives, conduct thorough assessments of their existing systems and processes, and establish a realistic implementation timeline. This stage also includes identifying key stakeholders, securing executive sponsorship, and building a dedicated project team.
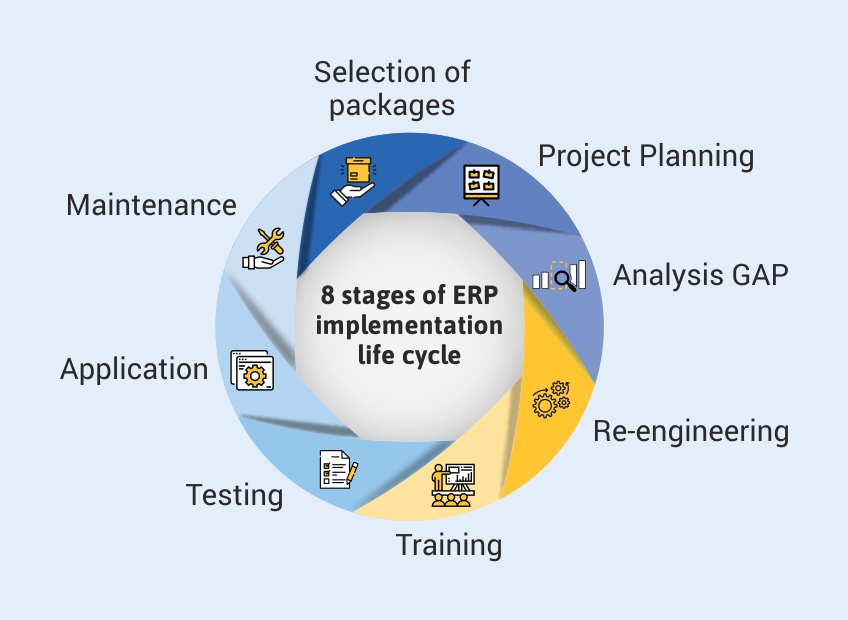
2. System Selection
With a solid plan in place, organizations embark on the critical task of selecting an ERP system that aligns with their specific needs and requirements. This involves evaluating various vendor solutions, conducting due diligence, and carefully considering factors such as functionality, scalability, cost, and vendor reputation.
3. Customization and Configuration
Once an ERP system is selected, it must be customized and configured to meet the unique requirements of the organization. This stage involves modifying the system’s settings, creating custom reports and dashboards, and integrating it with other business applications. Careful attention to detail is essential to ensure that the system aligns seamlessly with existing processes and workflows.
4. Data Migration
Data migration is a critical step in the ERP implementation life cycle that requires meticulous planning and execution. Organizations must extract data from their legacy systems and migrate it to the new ERP system. This process can be complex and time-consuming, and it requires careful data mapping, validation, and testing to ensure accuracy and integrity.
5. Testing and Training
Before going live with the new ERP system, it is essential to conduct thorough testing to identify and resolve any potential issues. This involves user acceptance testing, system integration testing, and performance testing. Additionally, comprehensive training programs must be provided to ensure that users are proficient in operating the new system.
6. Go-Live and Stabilization
The go-live phase marks the transition to the new ERP system. This stage requires careful monitoring and support to ensure a smooth transition and minimize disruptions. Organizations must establish clear communication channels, provide ongoing training, and address any issues that may arise during the stabilization period.
7. Continuous Improvement
ERP implementation is not a one-time event; it is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement. Organizations must regularly evaluate their system’s performance, identify areas for optimization, and implement updates and upgrades to maintain its effectiveness. This iterative approach ensures that the ERP system remains aligned with the organization’s evolving needs and delivers ongoing value.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ERP Implementation Life Cycle
Advantages:
- Improved efficiency: ERP systems streamline business processes, reduce manual tasks, and automate workflows, leading to significant efficiency gains.
- Enhanced data accuracy: ERP systems provide a single source of truth for all business data, eliminating data silos and ensuring data accuracy and consistency.
- Increased visibility and control: ERP systems offer real-time visibility into all aspects of the business, enabling better decision-making and improved control over operations.
- Improved customer service: ERP systems provide a 360-degree view of customer interactions, enabling organizations to respond quickly to customer inquiries and provide personalized service.
- Reduced costs: By automating processes and eliminating inefficiencies, ERP systems can help organizations reduce operating costs and improve profitability.
Disadvantages:
- High implementation costs: ERP implementation can be a costly and time-consuming process, requiring significant investments in software, hardware, and consulting services.
- Complexity: ERP systems are complex and require extensive customization and configuration to meet specific business needs, which can be challenging for organizations with limited resources.
- Potential disruptions: ERP implementation can disrupt business operations during the transition period, leading to temporary productivity losses and customer dissatisfaction.
- Resistance to change: Employees may resist adopting new technologies and processes, which can hinder the successful implementation of ERP systems.
- Ongoing maintenance and upgrades: ERP systems require ongoing maintenance and upgrades to ensure optimal performance and security, which can add to the total cost of ownership.
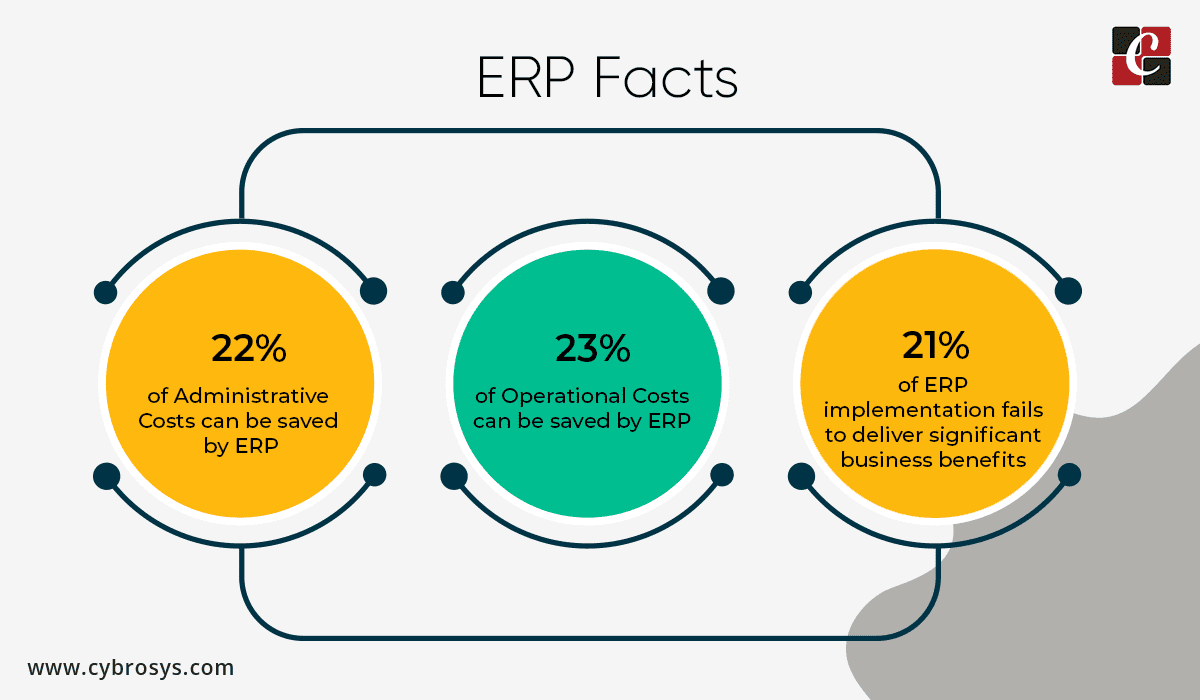
Summary of ERP Implementation Life Cycle
The ERP implementation life cycle consists of the following key stages:
- Planning and Assessment
- System Selection
- Customization and Configuration
- Data Migration
- Testing and Training
- Go-Live and Stabilization
- Continuous Improvement
Q&A on ERP Implementation Life Cycle
1. What is the most important factor to consider when selecting an ERP system?
Alignment with business objectives and specific requirements.
2. How can organizations minimize disruptions during ERP implementation?
Thorough planning, effective communication, and comprehensive training.
3. What is the role of data migration in the ERP implementation process?
To transfer data from legacy systems to the new ERP system, ensuring accuracy and integrity.
4. Why is it important to involve key stakeholders in the ERP implementation process?
To gain buy-in, secure resources, and ensure alignment with organizational goals.
5. What are the benefits of continuous improvement in ERP implementation?
To maintain system effectiveness, address evolving needs, and maximize value over time.
6. How can organizations overcome resistance to change during ERP implementation?
Through effective communication, training, and involvement of users in the process.
7. What is the typical timeline for an ERP implementation project?
Varies depending on the size and complexity of the organization and the chosen ERP system.
8. How can organizations ensure a successful ERP implementation?
By following best practices, engaging experienced consultants, and securing executive sponsorship.
9. What are the key challenges associated with ERP implementation?
High costs, complexity, potential disruptions, and resistance to change.
10. How can organizations measure the ROI of ERP implementation?
By tracking improvements in efficiency, data accuracy, customer service, and cost reduction.
11. What are the emerging trends in ERP implementation?
Cloud-based ERP, artificial intelligence, and data analytics.
12. How can organizations avoid common pitfalls in ERP implementation?
Through thorough planning, realistic timelines, and effective risk management.
13. What is the future of ERP implementation?
Continued adoption of cloud-based solutions, increased integration with other technologies, and a focus on data-driven decision-making.
Conclusion
The ERP implementation life cycle is a critical journey that can transform business operations and drive significant value. By understanding the intricacies of each stage, organizations can navigate this complex process successfully and reap the benefits of improved efficiency, enhanced data accuracy, increased visibility and control, improved customer service, and reduced costs.
Rebuttal
Some may argue that ERP implementation is too costly and complex for small and medium-sized businesses. However, modern cloud-based ERP solutions have made these systems more accessible and affordable for organizations of all sizes. With the right planning and implementation strategy, businesses can minimize the challenges and maximize the value of ERP systems, unlocking new opportunities for growth and success.
