Embark on a Transformative Journey: Unlocking the Value of ERP for Your Small Business
In the ever-evolving landscape of business, small enterprises face a myriad of challenges that can hinder their growth and success. From managing complex operations to streamlining processes, the need for a robust and efficient solution has become paramount. Enter Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, designed to revolutionize the way small businesses operate and empower them to thrive in today’s competitive market.
ERP systems serve as the backbone of a small business, seamlessly integrating various aspects of operations, including finance, supply chain management, customer relationship management (CRM), and human resources. By consolidating these functions into a single, unified platform, ERP systems provide businesses with a comprehensive view of their operations, enabling them to make informed decisions, optimize processes, and drive growth.
Unveiling the Value Proposition: ERP as a Catalyst for Small Business Success
The value proposition of ERP systems for small businesses is multifaceted, offering a range of benefits that can transform their operations and drive success. Here are the key value propositions that make ERP systems an indispensable investment for small businesses:

-
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: ERP systems automate and streamline business processes, reducing manual tasks, eliminating redundancies, and improving overall operational efficiency. This translates into significant time and cost savings, allowing businesses to focus on more strategic initiatives that drive growth.
-
Improved Data Management and Reporting: ERP systems provide a centralized repository for all business data, ensuring data integrity and accuracy. This enables businesses to generate comprehensive reports and gain real-time insights into their performance, empowering them to make data-driven decisions that drive profitability.
-
Enhanced Customer Relationship Management: ERP systems integrate CRM capabilities, providing businesses with a holistic view of customer interactions. This enables them to track customer preferences, manage customer orders, and provide personalized experiences, fostering stronger customer relationships and driving loyalty.
-
Improved Supply Chain Management: ERP systems optimize supply chain operations, enabling businesses to manage inventory levels, track shipments, and automate procurement processes. This enhances supply chain visibility, reduces lead times, and minimizes the risk of stockouts, leading to improved customer satisfaction and profitability.
-
Increased Collaboration and Communication: ERP systems foster collaboration and communication among different departments within a small business. By providing a shared platform for data and information, ERP systems break down departmental silos and promote cross-functional alignment, leading to improved decision-making and increased productivity.
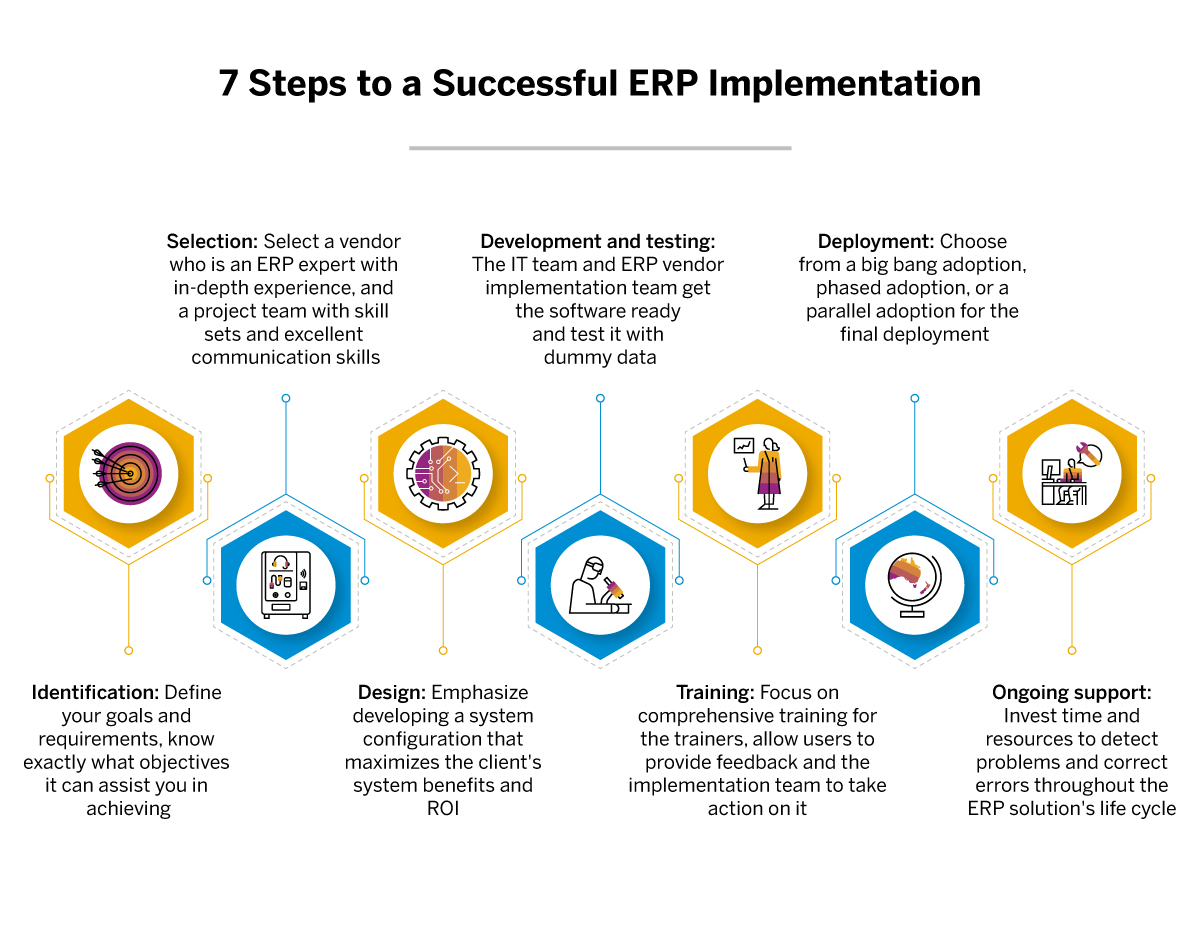
Addressing the Pain Points of Small Business Owners: ERP as a Solution
Small business owners face a unique set of pain points that can hinder their growth and success. ERP systems are designed to address these pain points, providing solutions that alleviate challenges and empower businesses to thrive. Here are some of the key pain points that ERP systems effectively address:
-
Limited Visibility into Business Operations: Small business owners often lack a comprehensive view of their operations, making it difficult to identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions. ERP systems provide real-time visibility into all aspects of the business, enabling owners to make data-driven decisions that drive growth.
-
Inefficient Processes and Redundancies: Manual processes and fragmented systems can lead to inefficiencies and redundancies, wasting time and resources. ERP systems automate and streamline processes, eliminating redundancies and improving overall operational efficiency, freeing up resources for more strategic initiatives.

-
Lack of Data Integrity and Accuracy: Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to poor decision-making and missed opportunities. ERP systems provide a centralized repository for all business data, ensuring data integrity and accuracy, enabling businesses to make informed decisions based on reliable information.
-
Limited Scalability and Growth Potential: Small businesses often face challenges in scaling their operations due to fragmented systems and limited capacity. ERP systems are designed to be scalable, supporting growth and expansion without the need for costly and time-consuming upgrades.
-
Poor Customer Relationship Management: Ineffective customer relationship management can lead to lost customers and missed opportunities. ERP systems integrate CRM capabilities, enabling businesses to track customer interactions, manage customer orders, and provide personalized experiences, fostering stronger customer relationships and driving loyalty.
Exploring the Advantages and Disadvantages of ERP for Small Businesses
While ERP systems offer a range of benefits for small businesses, it’s important to consider both the advantages and disadvantages before making an investment. Here’s a detailed discussion of the advantages and disadvantages of ERP systems for small businesses:
Advantages of ERP for Small Businesses:
-
Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: ERP systems automate and streamline business processes, reducing manual tasks, eliminating redundancies, and improving overall operational efficiency. This translates into significant time and cost savings, allowing businesses to focus on more strategic initiatives that drive growth.
-
Improved Data Management and Reporting: ERP systems provide a centralized repository for all business data, ensuring data integrity and accuracy. This enables businesses to generate comprehensive reports and gain real-time insights into their performance, empowering them to make data-driven decisions that drive profitability.
-
Enhanced Customer Relationship Management: ERP systems integrate CRM capabilities, providing businesses with a holistic view of customer interactions. This enables them to track customer preferences, manage customer orders, and provide personalized experiences, fostering stronger customer relationships and driving loyalty.
-
Improved Supply Chain Management: ERP systems optimize supply chain operations, enabling businesses to manage inventory levels, track shipments, and automate procurement processes. This enhances supply chain visibility, reduces lead times, and minimizes the risk of stockouts, leading to improved customer satisfaction and profitability.
-
Increased Collaboration and Communication: ERP systems foster collaboration and communication among different departments within a small business. By providing a shared platform for data and information, ERP systems break down departmental silos and promote cross-functional alignment, leading to improved decision-making and increased productivity.
-
Scalability and Growth Potential: ERP systems are designed to be scalable, supporting growth and expansion without the need for costly and time-consuming upgrades. This enables small businesses to invest in a solution that can grow with them, supporting their future growth plans.
Disadvantages of ERP for Small Businesses:
-
Cost of Implementation: ERP systems can be expensive to implement, requiring significant upfront investment. Small businesses with limited resources may need to carefully consider the cost of implementation and ensure they have the budget to support the project.
-
Complexity and Customization: ERP systems can be complex to implement and customize, requiring specialized knowledge and expertise. Small businesses may need to invest in training and support to ensure the system is properly implemented and configured to meet their specific needs.
-
Time Required for Implementation: ERP implementation can be a time-consuming process, requiring significant resources and effort. Small businesses may need to allocate dedicated staff or hire external consultants to manage the implementation process and minimize disruption to ongoing operations.
-
Data Migration Challenges: Migrating data from existing systems to an ERP system can be challenging and time-consuming. Small businesses may need to invest in data cleansing and migration services to ensure the accuracy and integrity of their data.
-
Ongoing Maintenance and Support: ERP systems require ongoing maintenance and support to ensure they are operating at optimal performance. Small businesses may need to factor in the cost of ongoing support and maintenance when evaluating the total cost of ownership.
Summary of ERP for Small Businesses: Key Takeaways
ERP systems offer a range of benefits for small businesses, including enhanced efficiency, improved data management, enhanced customer relationship management, improved supply chain management, increased collaboration and communication, scalability, and growth potential. While there are some disadvantages to consider, such as cost of implementation, complexity and customization, time required for implementation, data migration challenges, and ongoing maintenance and support, the benefits of ERP systems often outweigh the disadvantages for small businesses that are looking to grow and succeed.
Q&A: Frequently Asked Questions about ERP for Small Businesses
Q1: What is the most significant benefit of an ERP system for a small business?
A1: The most significant benefit of an ERP system for a small business is the ability to streamline and automate business processes, leading to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved productivity.
Q2: How can an ERP system improve data management for a small business?
A2: ERP systems provide a centralized repository for all business data, ensuring data integrity and accuracy. This enables businesses to generate comprehensive reports and gain real-time insights into their performance, empowering them to make data-driven decisions that drive profitability.
Q3: How can an ERP system help a small business manage customer relationships more effectively?
A3: ERP systems integrate CRM capabilities, providing businesses with a holistic view of customer interactions. This enables them to track customer preferences, manage customer orders, and provide personalized experiences, fostering stronger customer relationships and driving loyalty.
Q4: How can an ERP system optimize supply chain management for a small business?
A4: ERP systems optimize supply chain operations, enabling businesses to manage inventory levels, track shipments, and automate procurement processes. This enhances supply chain visibility, reduces lead times, and minimizes the risk of stockouts, leading to improved customer satisfaction and profitability.
Q5: How can an ERP system foster collaboration and communication within a small business?
A5: ERP systems provide a shared platform for data and information, breaking down departmental silos and promoting cross-functional alignment. This fosters collaboration and communication among different departments, leading to improved decision-making and increased productivity.
Q6: What are the key considerations for small businesses when evaluating ERP systems?
A6: Key considerations for small businesses when evaluating ERP systems include cost of implementation, complexity and customization, time required for implementation, data migration challenges, and ongoing maintenance and support.
Q7: What are the common challenges faced by small businesses during ERP implementation?
A7: Common challenges faced by small businesses during ERP implementation include data migration, process re-engineering, user adoption, and change management.
Q8: How can small businesses mitigate the risks associated with ERP implementation?
A8: Small businesses can
