Unlocking Efficiency and Profitability: A Comprehensive Guide to Manufacturing ERP Software
 .
.
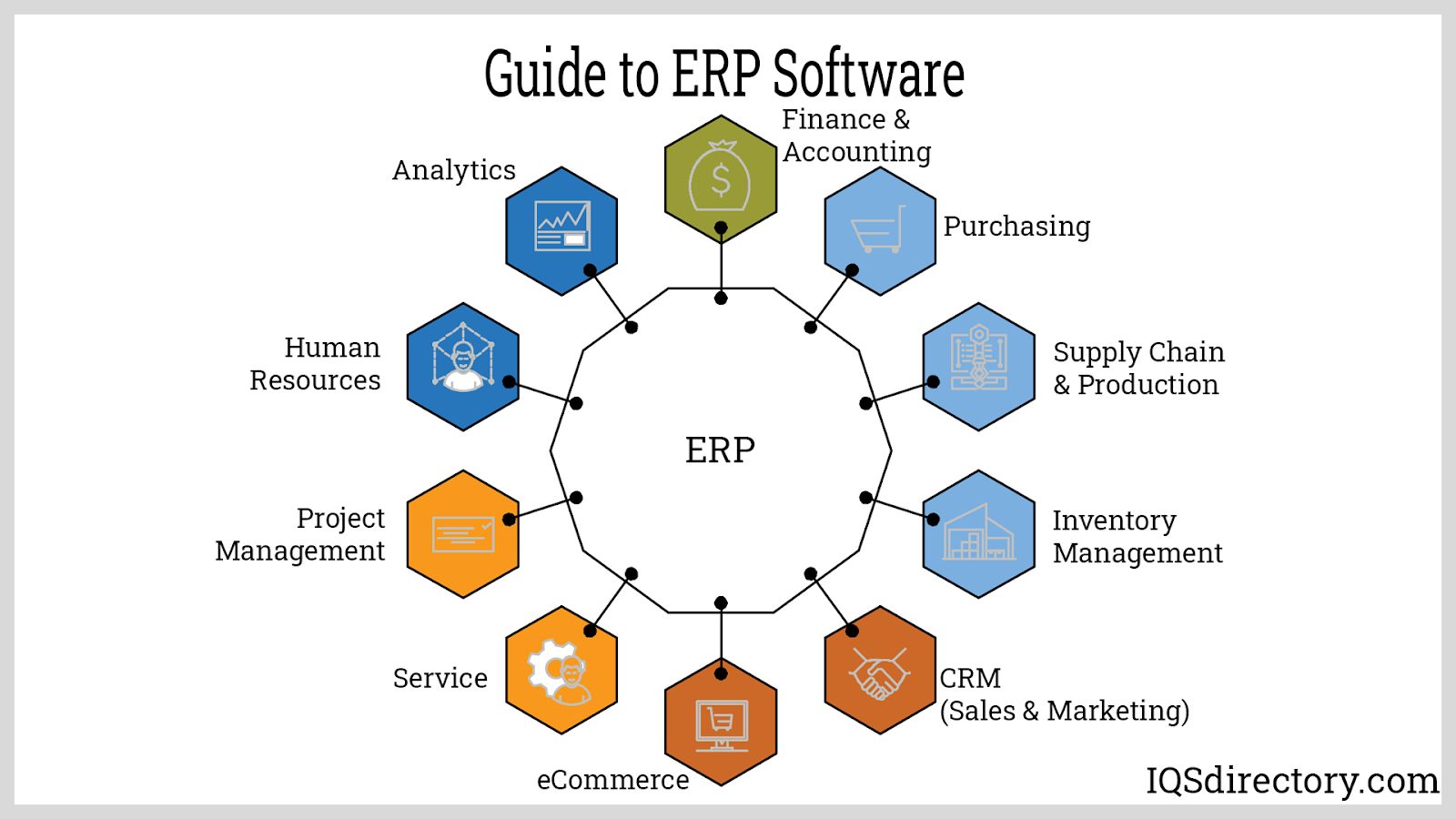
Welcome to the world of manufacturing, a dynamic and ever-evolving landscape where efficiency and profitability are paramount. In this complex ecosystem, where intricate processes and intricate supply chains intertwine, navigating the intricacies of production, inventory, and customer fulfillment can feel like a daunting task. Enter Manufacturing ERP software, a technological beacon illuminating the path to streamlined operations, enhanced productivity, and ultimately, greater success.
Imagine a single, centralized platform that seamlessly integrates all facets of your manufacturing business. This is the promise of Manufacturing ERP software, a solution designed to empower manufacturers by providing real-time insights, automating crucial processes, and facilitating data-driven decision-making. It’s a powerful tool that can transform your operations, enabling you to navigate the challenges of today’s competitive manufacturing landscape with confidence.
At its core, Manufacturing ERP software acts as the central nervous system of your manufacturing enterprise. It connects all your critical business functions, from production planning and scheduling to inventory management, quality control, and customer relationship management. This integrated approach eliminates silos, fosters collaboration, and ensures that information flows freely throughout your organization.
But the benefits of Manufacturing ERP software extend far beyond mere integration. It empowers you to optimize every stage of your manufacturing journey, from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished goods. With real-time data at your fingertips, you gain a comprehensive understanding of your operations, enabling you to identify bottlenecks, anticipate demand fluctuations, and make informed decisions that drive efficiency and profitability.
 .
.
Manufacturing ERP software is not a one-size-fits-all solution. It’s a versatile tool that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of your business, regardless of size or industry. Whether you’re a small-scale manufacturer focused on niche markets or a large-scale enterprise with global operations, there’s a Manufacturing ERP solution designed to empower your growth and success.
The power of Manufacturing ERP software lies in its ability to automate repetitive tasks, freeing up your valuable time and resources to focus on strategic initiatives. From generating purchase orders to scheduling production runs, the software handles the mundane details, allowing your team to concentrate on innovation, customer engagement, and driving business growth.
As your manufacturing business evolves, so too does the need for adaptable and scalable solutions. Manufacturing ERP software is designed to grow with you, seamlessly accommodating changes in your operations, product offerings, and market demands. This scalability ensures that you always have the right tools to navigate the ever-changing landscape of the manufacturing industry.
Navigating the Manufacturing ERP Landscape: A Comprehensive Overview
The world of Manufacturing ERP software is a diverse one, offering a wide range of solutions to cater to the unique needs of different manufacturing businesses. Understanding the key components and functionalities of these systems is crucial to selecting the right solution for your specific requirements.
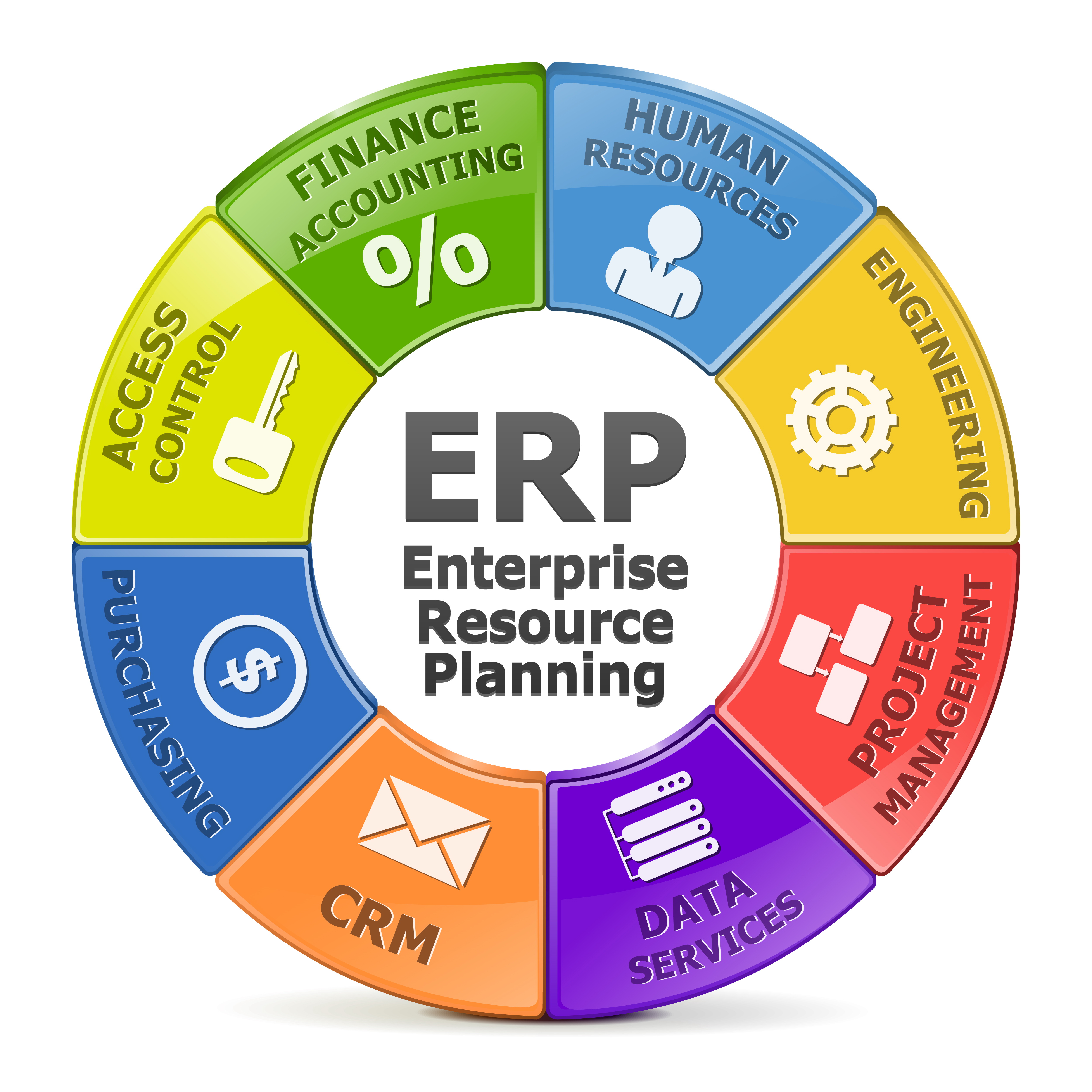
1. Production Planning and Scheduling: Orchestrating the Manufacturing Process
 .
.
At the heart of any manufacturing operation lies the ability to plan and schedule production effectively. Manufacturing ERP software provides a robust platform for optimizing this critical process, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently and production runs smoothly.
a) Demand Forecasting and Planning:
Manufacturing ERP software empowers you to accurately forecast demand, taking into account historical sales data, seasonal trends, and market fluctuations. This data-driven approach allows you to anticipate customer needs and adjust production plans accordingly, minimizing stockouts and maximizing production efficiency.
b) Material Requirements Planning (MRP):
MRP is a core functionality of Manufacturing ERP software, ensuring that the right materials are available at the right time to meet production demands. By analyzing production schedules and inventory levels, MRP automatically generates purchase orders for raw materials, ensuring a seamless flow of materials throughout the manufacturing process.
 .
.
c) Production Scheduling and Optimization:
Manufacturing ERP software streamlines the production scheduling process, enabling you to optimize resource allocation, minimize downtime, and maximize throughput. The software considers factors such as machine availability, labor capacity, and production lead times to create efficient production schedules, ensuring timely delivery of finished goods.
d) Capacity Planning and Management:
Capacity planning is crucial for ensuring that your production facilities have the resources to meet demand. Manufacturing ERP software provides tools for analyzing production capacity, identifying potential bottlenecks, and optimizing resource utilization. This allows you to proactively address capacity constraints and avoid delays in production.
e) Real-Time Monitoring and Control:
 .
.
Manufacturing ERP software offers real-time visibility into production processes, enabling you to track progress, identify deviations from planned schedules, and take corrective action quickly. This real-time monitoring empowers you to maintain control over your production operations, ensuring on-time delivery and meeting customer expectations.
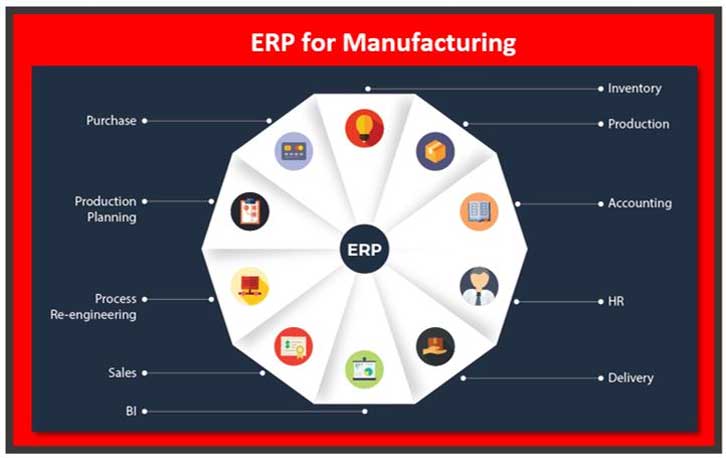
2. Inventory Management: Optimizing Stock Levels and Reducing Costs
Effective inventory management is a cornerstone of efficient manufacturing operations. Manufacturing ERP software provides a comprehensive suite of tools for managing inventory levels, minimizing waste, and reducing costs.
a) Inventory Tracking and Control:
Manufacturing ERP software provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, enabling you to track the movement of materials throughout the supply chain. This granular level of detail allows you to identify potential stockouts, optimize inventory levels, and minimize waste.
 .
.
b) Warehouse Management:
For businesses with extensive warehouse operations, Manufacturing ERP software offers dedicated modules for managing warehouse activities. These modules streamline processes such as receiving, picking, packing, and shipping, optimizing warehouse space utilization and minimizing handling costs.
c) Lot and Serial Number Tracking:
For industries with stringent quality control requirements, Manufacturing ERP software enables lot and serial number tracking. This functionality allows you to trace the origin of materials and products, ensuring compliance with regulations and facilitating product recalls if necessary.
d) Inventory Optimization and Forecasting:
Manufacturing ERP software employs advanced algorithms to optimize inventory levels, minimizing holding costs and reducing the risk of stockouts. By analyzing historical data and demand patterns, the software can predict future inventory needs, ensuring that the right amount of materials is available at the right time.
e) Automated Ordering and Procurement:
Manufacturing ERP software automates the procurement process, streamlining the ordering of raw materials and supplies. The software automatically generates purchase orders based on inventory levels and production schedules, reducing manual effort and minimizing delays in material procurement.
3. Quality Control and Assurance: Maintaining Excellence in Manufacturing
Quality control is paramount in the manufacturing industry, ensuring that products meet customer expectations and comply with industry standards. Manufacturing ERP software provides a range of tools for managing quality control processes, minimizing defects, and enhancing product quality.
a) Quality Management System (QMS):
Manufacturing ERP software integrates with a QMS, providing a centralized platform for managing quality control procedures, documenting processes, and tracking quality data. This integrated approach ensures that quality standards are consistently met throughout the manufacturing process.
b) Inspection and Testing Management:
Manufacturing ERP software enables the management of inspection and testing processes, ensuring that products meet quality standards at every stage of production. The software allows you to define inspection criteria, record test results, and track deviations from quality specifications.
c) Non-Conformance Management:
When deviations from quality standards are detected, Manufacturing ERP software facilitates the management of non-conformance issues. The software allows you to investigate root causes, implement corrective actions, and prevent similar issues from recurring.
d) Supplier Quality Management:
Manufacturing ERP software extends quality control to your supply chain, enabling you to manage supplier performance and ensure that materials meet your quality standards. The software allows you to track supplier performance metrics, conduct audits, and approve suppliers based on their quality record.
e) Continuous Improvement and Analysis:
Manufacturing ERP software provides tools for analyzing quality data, identifying trends, and implementing continuous improvement initiatives. By tracking quality metrics over time, you can identify areas for improvement and optimize your manufacturing processes to enhance product quality and reduce defects.
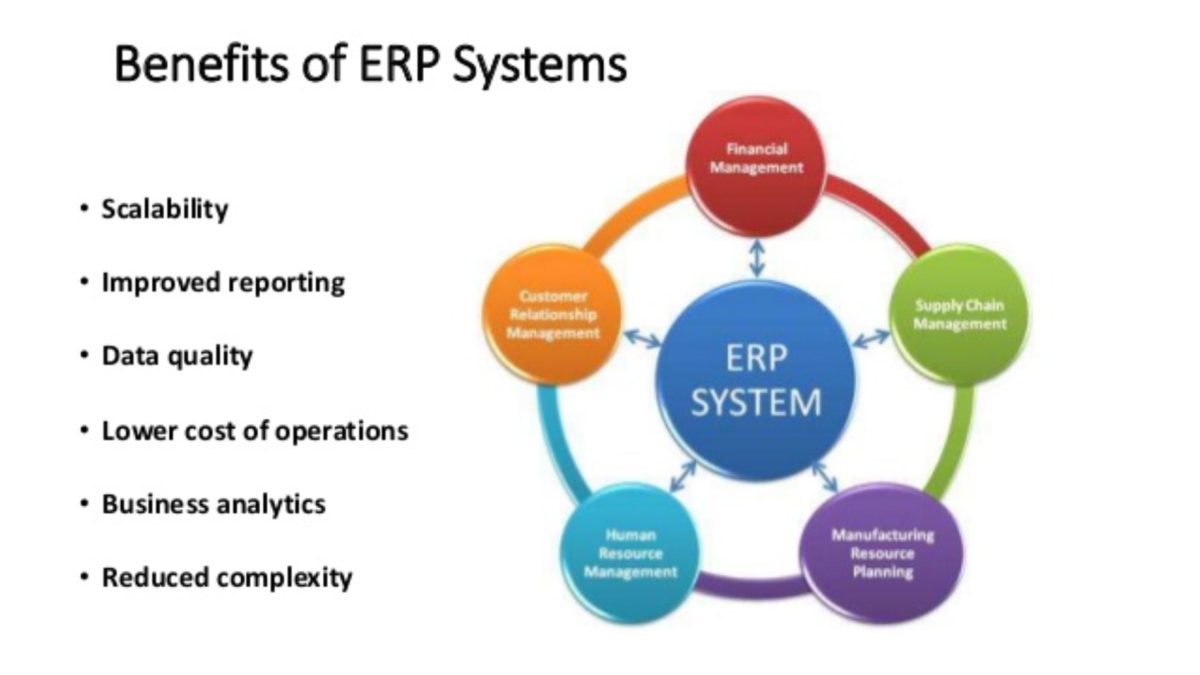
4. Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Fostering Customer Loyalty and Growth
Building strong customer relationships is essential for long-term success in the manufacturing industry. Manufacturing ERP software integrates with CRM systems, providing a comprehensive platform for managing customer interactions, improving communication, and fostering customer loyalty.
a) Customer Data Management:
Manufacturing ERP software centralizes customer data, providing a single source of truth for all customer information. This data includes contact details, purchase history, service records, and communication preferences, enabling you to personalize interactions and provide exceptional customer service.
b) Sales and Marketing Automation:
Manufacturing ERP software automates sales and marketing processes, enabling you to reach out to customers effectively, track leads, and nurture relationships. The software can automate tasks such as sending email campaigns, generating quotes, and managing customer interactions.
c) Order Management and Fulfillment:
Manufacturing ERP software streamlines the order management process, from order entry to delivery. The software tracks order status, manages inventory levels, and ensures timely fulfillment, providing customers with real-time updates on their orders.
d) Customer Service and Support:
Manufacturing ERP software integrates with customer service and support systems, enabling you to provide prompt and efficient assistance to customers. The software can track customer inquiries, manage support tickets, and provide access to relevant product information.
e) Customer Feedback and Analysis:
Manufacturing ERP software allows you to collect and analyze customer feedback, identifying areas for improvement and enhancing customer satisfaction. The software can track customer surveys, reviews, and social media mentions, providing valuable insights into customer sentiment.
5. Financial Management: Gaining Insights and Optimizing Performance
Financial management is a critical aspect of any manufacturing business. Manufacturing ERP software integrates with accounting and financial systems, providing a comprehensive platform for managing finances, tracking costs, and optimizing profitability.
a) Cost Accounting and Tracking:
Manufacturing ERP software enables detailed cost accounting, allowing you to track the costs associated with each stage of the manufacturing process. This information provides valuable insights into production costs, enabling you to identify areas for cost optimization and improve profitability.
b) Budgeting and Forecasting:
Manufacturing ERP software facilitates budgeting and forecasting, enabling you to plan for future expenses and revenue streams. The software can analyze historical data, project future trends, and generate financial reports, providing a clear picture of your financial health.
c) Financial Reporting and Analysis:
Manufacturing ERP software provides a range of financial reporting tools, enabling you to generate detailed reports on key performance indicators (KPIs), financial statements, and other financial data. This information allows you to monitor financial performance, identify trends, and make informed business decisions.
d) Cash Flow Management:
Manufacturing ERP software helps you manage cash flow, ensuring that you have sufficient funds to meet your financial obligations. The software can track receivables, payables, and other cash flow activities, enabling you to optimize working capital and avoid liquidity issues.
e) Regulatory Compliance:
Manufacturing ERP software helps you comply with financial regulations, ensuring that your financial records are accurate and auditable. The software can automate tasks such as tax reporting and financial statement preparation, reducing the risk of errors and penalties.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Manufacturing ERP Software
Manufacturing ERP software offers a wide range of benefits for manufacturers, streamlining operations, enhancing efficiency, and driving profitability. However, it’s essential to weigh the advantages against potential drawbacks before implementing an ERP solution.
Advantages of Manufacturing ERP Software:
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity:
Manufacturing ERP software automates repetitive tasks, freeing up valuable time and resources for strategic initiatives. By streamlining processes and eliminating manual tasks, the software significantly enhances efficiency and productivity, allowing your team to focus on high-value activities.
2. Improved Visibility and Control:
Manufacturing ERP software provides real-time visibility into all aspects of your operations, from production planning and scheduling to inventory management and customer relationships. This comprehensive view enables you to monitor progress, identify bottlenecks, and make informed decisions to optimize performance.
3. Reduced Costs and Waste:
By optimizing inventory levels, automating processes, and minimizing errors, Manufacturing ERP software helps you reduce costs and waste throughout your operations. This leads to increased profitability and a more sustainable business model.
4. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication:
Manufacturing ERP software facilitates collaboration and communication across departments, breaking down silos and ensuring that everyone is working towards common goals. This fosters a more cohesive and efficient work environment.
5. Improved Decision-Making:
Manufacturing ERP software provides access to real-time data and analytics, empowering you to make informed decisions based on facts rather than intuition. This data-driven approach leads to more strategic planning, improved resource allocation, and better business outcomes.
6. Increased Agility and Adaptability:
Manufacturing ERP software is designed to be scalable and adaptable, enabling you to adjust your operations to meet changing market demands and business needs. This agility allows you to respond quickly to opportunities and challenges, maintaining a competitive edge.
7. Improved Customer Satisfaction:
By streamlining operations, reducing errors, and providing real-time visibility into order status, Manufacturing ERP software enhances customer satisfaction. This leads to increased loyalty, repeat business, and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
Disadvantages of Manufacturing ERP Software:
1. High Initial Investment:
Implementing a Manufacturing ERP system can be a significant investment, requiring upfront costs for software licenses, hardware, and professional services. This cost can be a barrier for smaller businesses with limited budgets.
2. Complex Implementation and Training:
Implementing a Manufacturing ERP system can be a complex process, requiring careful planning, data migration, and user training. This can be time-consuming and require significant effort from your team.
3. Data Integration Challenges:
Integrating Manufacturing ERP software with existing systems can be challenging, requiring careful planning and technical expertise. This can lead to data inconsistencies and potential integration issues.
4. Resistance to Change:
Employees may resist the adoption of a new ERP system, fearing job displacement or changes to their work processes. Effective communication, training, and change management strategies are essential to overcome this resistance.
5. System Customization and Maintenance:
Customizing a Manufacturing ERP system to meet your specific needs can be expensive and time-consuming. Ongoing maintenance and updates are also required to ensure system security and functionality.
6. Dependence on Technology:
Implementing a Manufacturing ERP system creates a dependence on technology. If the system experiences downtime or technical issues, it can disrupt operations and impact productivity.
7. Limited Flexibility:
While Manufacturing ERP software offers a wide range of functionalities, it may not always be flexible enough to accommodate unique business processes or niche requirements. This can lead to limitations in adapting the system to specific workflows.
Choosing the Right Manufacturing ERP Software: A Step-by-Step Guide
Selecting the right Manufacturing ERP software for your business is a critical decision that can have a significant impact on your operations and success. This process requires careful consideration of your specific needs, budget, and long-term goals.
1. Define Your Business Requirements:
Start by clearly defining your business needs and objectives. What are your key challenges? What processes do you want to improve? What are your goals for efficiency, productivity, and profitability?
2. Research and Compare ERP Solutions:
Once you have a clear understanding of your requirements, research different Manufacturing ERP solutions available in the market. Consider factors such as functionality, industry specialization, pricing, and vendor reputation.
3. Conduct Proof-of-Concept (POC):
Before committing to a specific ERP solution, conduct a POC to evaluate its functionality and suitability for your business. This involves testing the software in a controlled environment with real-world data.
4. Assess Vendor Support and Training:
Consider the level of vendor support and training provided with the ERP solution. You need a vendor that offers comprehensive support, documentation, and training resources to ensure a smooth implementation and ongoing success.
5. Evaluate Cost and Return on Investment (ROI):
Calculate the total cost of ownership (TCO) for each ERP solution, including software licenses, hardware, implementation services, and ongoing maintenance. Assess the potential ROI based on expected cost savings, efficiency gains, and improved profitability.
6. Seek Expert Advice:
Consult with industry experts or consultants specializing in ERP implementation to get unbiased advice and guidance. They can help you evaluate different solutions, assess risks, and develop a successful implementation plan.
7. Make an Informed Decision:
Based on your research, POC results, and expert advice, make an informed decision on the ERP solution that best meets your business needs and goals.
Implementing Manufacturing ERP Software: A Roadmap to Success
Implementing a Manufacturing ERP system is a complex process that requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing management. Here’s a roadmap to ensure a successful implementation:
1. Define Implementation Scope and Objectives:
Clearly define the scope and objectives of your ERP implementation project. What modules will be implemented? What are the key business processes to be automated? What are the desired outcomes?
2. Assemble a Project Team:
Form a dedicated project team with representatives from key departments, including IT, operations, finance, and sales. This team will be responsible for planning, executing, and managing the implementation process.
3. Develop a Detailed Implementation Plan:
Create a comprehensive implementation plan outlining timelines, milestones, responsibilities, and resources. This plan should be reviewed and updated regularly to ensure progress and address any challenges.
4. Data Migration and Cleansing:
Carefully plan and execute data migration from existing systems to the new ERP platform. Ensure data accuracy, consistency, and completeness to avoid future issues.
5. System Configuration and Customization:
Configure and customize the ERP system to meet your specific business requirements. This may involve tailoring workflows, reports, and user interfaces.
6. User Training and Adoption:
Provide comprehensive training to all users on the new ERP system. This training should cover system functionalities, workflows, and best practices.
7. Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support:
Plan a phased go-live approach to minimize disruption to your operations. Provide ongoing post-implementation support to address user issues, troubleshoot problems, and ensure system stability.
The Future of Manufacturing ERP Software: Trends and Innovations
The manufacturing industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer demands, and global competition. Manufacturing ERP software is evolving alongside, incorporating new technologies and functionalities to address the challenges and opportunities of the future.
1. Cloud-Based ERP Solutions:
Cloud-based ERP solutions are gaining popularity, offering flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Cloud solutions eliminate the need for on-premises infrastructure, making them ideal for businesses of all sizes.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
AI and ML are transforming Manufacturing ERP software, enabling predictive analytics, automated decision-making, and improved process optimization. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict future trends, and optimize operations.
3. Internet of Things (IoT) Integration:
IoT integration is connecting Manufacturing ERP software to real-time data from sensors and devices on the factory floor. This data provides valuable insights into production processes, equipment performance, and product quality.
4. Blockchain Technology:
Blockchain technology is emerging as a solution for enhancing supply chain transparency, traceability, and security. Manufacturing ERP software is incorporating blockchain functionalities to track materials, products, and transactions across the supply chain.
5. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR):
AR and VR are enhancing training, maintenance, and design processes in manufacturing. Manufacturing ERP software is integrating AR and VR functionalities to provide immersive training experiences, visualize complex designs, and guide maintenance operations.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Manufacturing ERP Software
1. What is the difference between ERP and MRP software?
MRP (Material Requirements Planning) is a subset of ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning). MRP focuses specifically on managing materials and production planning, while ERP encompasses a wider range of business functions, including finance, sales, marketing, and customer service.
2. How much does Manufacturing ERP software cost?
The cost of Manufacturing ERP software varies depending on factors such as the size of your business, the features you require, and the vendor you choose. Cloud-based solutions typically have lower upfront costs but may involve recurring subscription fees.
3. What are the key benefits of implementing a Manufacturing ERP system?
Key benefits include enhanced efficiency and productivity, improved visibility and control, reduced costs and waste, enhanced collaboration and communication, improved decision-making, increased agility and adaptability, and improved customer satisfaction.
4. What are the challenges of implementing a Manufacturing ERP system?
Challenges include high initial investment, complex implementation and training, data integration challenges, resistance to change, system customization and maintenance, dependence on technology, and limited flexibility.
5. How long does it take to implement a Manufacturing ERP system?
The implementation timeframe varies depending on the size and complexity of your business, the chosen ERP solution, and the level of customization required. It can take anywhere from a few months to a year or more.
6. What are the best practices for choosing a Manufacturing ERP vendor?
Key considerations include vendor reputation, industry expertise, customer support, implementation experience, and pricing. It’s also important to assess the vendor’s commitment to innovation and ongoing support.
7. How can I ensure a successful ERP implementation?
A successful implementation requires careful planning, strong project management, effective communication, and ongoing user training. It’s also essential to involve key stakeholders from different departments and to address any resistance to change.
8. What are the future trends in Manufacturing ERP software?
Future trends include cloud-based solutions, AI and ML integration, IoT connectivity, blockchain technology, and AR/VR functionalities. These technologies are transforming Manufacturing ERP software to address the challenges and opportunities of the future.
9. What are the key performance indicators (KPIs) to track after implementing an ERP system?
Key KPIs include production efficiency, inventory turnover, on-time delivery rate, customer satisfaction, cost per unit, and return on investment (ROI).
10. How can I optimize my Manufacturing ERP system for maximum efficiency?
Optimize your system by regularly reviewing and updating workflows, automating tasks wherever possible, leveraging data analytics to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement, and providing ongoing user training to ensure effective utilization.
11. What are the best resources for learning more about Manufacturing ERP software?
Resources include industry publications, online forums, vendor websites, and ERP consulting firms. You can also attend industry conferences and webinars to stay up-to-date on the latest trends and innovations.
12. What are the common mistakes to avoid when implementing a Manufacturing ERP system?
Common mistakes include failing to define clear objectives, underestimating the implementation complexity, neglecting user training, rushing the go-live process, and failing to provide ongoing support.
13. How can I measure the success of my Manufacturing ERP implementation?
Measure success by tracking KPIs, analyzing operational improvements, and assessing the impact on profitability. You can also conduct user surveys to gauge satisfaction levels and identify areas for further optimization.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Manufacturing ERP Software
In the dynamic and competitive landscape of the manufacturing industry, embracing the power of Manufacturing ERP software is no longer a choice but a necessity. It’s a strategic investment that can unlock efficiency, drive profitability, and propel your business to new heights.
By automating processes, providing real-time insights, and fostering collaboration, Manufacturing ERP software empowers you to navigate the complexities of production, inventory, and customer fulfillment with confidence. It’s a versatile tool that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of your business, regardless of size or industry.
As you embark on your journey towards implementing a Manufacturing ERP system, remember that success requires careful planning, effective execution, and ongoing commitment. By following a structured approach, involving key stakeholders, and addressing potential challenges proactively, you can ensure a smooth implementation and reap the transformative benefits of this powerful technology.
Embrace the future of manufacturing with Manufacturing ERP software, a solution that empowers you to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and drive profitability. The journey ahead is filled with exciting opportunities, and with the right tools and strategies, you can navigate the complexities of the manufacturing landscape with confidence and achieve lasting success.
Disclaimer: This article provides general information about Manufacturing ERP software and should not be considered professional advice. The specific requirements and challenges of each business are unique, and it’s essential to consult with industry experts or consultants for tailored guidance. The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be interpreted as a substitute for professional advice.
 .
.

