Unlocking Efficiency and Growth: Finding the Best ERP System for Your Manufacturing Business
 .
.
Welcome, fellow manufacturers! In today’s competitive landscape, efficiency and agility are paramount to success. As you navigate the complexities of production, inventory management, and customer demands, the right ERP system can be your secret weapon. But with so many options available, choosing the best ERP for your manufacturing business can feel like searching for a needle in a haystack.
Fear not! This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and insights you need to make an informed decision. We’ll delve into the intricate world of ERP systems, exploring their functionalities, benefits, and considerations for your specific manufacturing needs.
Imagine a system that seamlessly integrates all your business processes, from raw material procurement to final product delivery. This is the power of a well-implemented ERP system. It streamlines operations, eliminates redundancies, and empowers you to make data-driven decisions. But finding the perfect fit requires careful analysis and understanding of your unique requirements.
This guide will act as your roadmap, guiding you through the complexities of ERP selection and implementation. We’ll discuss the key features to look for, the advantages and disadvantages of different ERP systems, and the crucial factors to consider during your evaluation process.
 .
.
We’ll also explore real-world examples of how manufacturers have leveraged ERP systems to achieve remarkable results. From streamlining production processes to optimizing inventory management, these success stories will inspire you and showcase the transformative power of ERP technology.
By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and confidence to identify the best ERP system for your manufacturing business. You’ll understand how to navigate the selection process, negotiate favorable terms, and ensure a smooth implementation for optimal results.
So, let’s embark on this journey together, and unlock the potential for efficiency, growth, and lasting success in your manufacturing operations.
The Essence of ERP Systems: A Comprehensive Overview
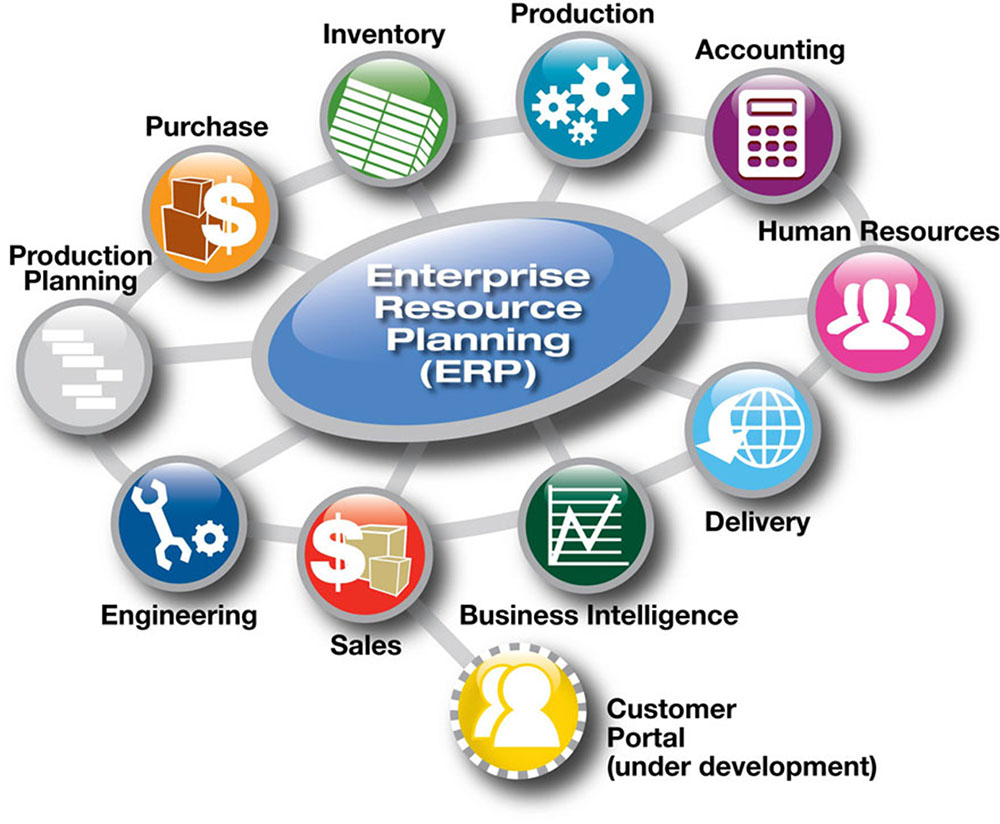
An ERP system, or Enterprise Resource Planning system, is a software suite that integrates various business processes within a single platform. It acts as a central hub for managing data, automating tasks, and providing real-time insights across departments.
For manufacturers, ERP systems offer a powerful solution to streamline operations, optimize resource allocation, and enhance overall efficiency. By connecting disparate departments such as production, inventory, sales, and finance, ERP systems create a unified view of the business, enabling informed decision-making and improved collaboration.
 .
.
Key Features of ERP Systems for Manufacturing
ERP systems for manufacturing are specifically designed to address the unique challenges and requirements of the industry. They offer a comprehensive set of features, including:
-
Production Planning and Scheduling: ERP systems enable manufacturers to plan production schedules, manage work orders, and track production progress in real-time. They provide tools for capacity planning, material requirements planning (MRP), and shop floor control.
 .
.
-
Inventory Management: ERP systems streamline inventory management processes, providing real-time visibility into stock levels, tracking material movements, and automating inventory replenishment. They help optimize inventory levels, minimize stockouts, and reduce storage costs.
 .
.
Quality Management: ERP systems support quality control processes, enabling manufacturers to track defects, manage non-conformances, and implement corrective actions. They provide tools for quality audits, documentation, and reporting.
-
Supply Chain Management: ERP systems facilitate efficient supply chain management by providing tools for supplier management, purchase order processing, and vendor performance tracking. They enhance visibility into the entire supply chain, enabling better collaboration with suppliers and reducing lead times.
-
Sales and Marketing: ERP systems integrate sales and marketing functions, enabling manufacturers to manage customer relationships, track sales orders, and generate sales reports. They support customer relationship management (CRM) functionalities and provide insights into customer behavior.
-
Financial Management: ERP systems provide financial management capabilities, including accounting, budgeting, and reporting. They streamline financial processes, automate tasks, and provide real-time financial insights.
-
Human Resources Management: Some ERP systems offer integrated human resource management (HRM) functionalities, allowing manufacturers to manage employee records, payroll, and benefits.
 .
.
Advantages of Implementing an ERP System for Manufacturing
Implementing an ERP system can bring numerous benefits to manufacturing businesses, including:
-
Improved Efficiency and Productivity: ERP systems automate repetitive tasks, eliminate manual processes, and streamline workflows, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
-
Enhanced Visibility and Control: ERP systems provide real-time visibility into all aspects of the business, enabling manufacturers to track performance, identify bottlenecks, and make informed decisions.
-
Better Inventory Management: ERP systems optimize inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and minimize storage costs. They provide real-time insights into inventory movements and help manufacturers make informed purchasing decisions.
-
Improved Customer Satisfaction: ERP systems enable manufacturers to deliver products on time and meet customer expectations. They streamline order processing, improve communication, and provide better customer service.
-
Reduced Costs: ERP systems can help manufacturers reduce costs by optimizing resource allocation, eliminating redundancies, and improving efficiency.
-
Enhanced Decision-Making: ERP systems provide real-time data and analytics, enabling manufacturers to make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information.
-
Improved Compliance and Risk Management: ERP systems help manufacturers comply with industry regulations and standards. They provide tools for tracking compliance, managing risks, and ensuring data security.
Disadvantages of Implementing an ERP System for Manufacturing
While ERP systems offer numerous benefits, there are also potential disadvantages to consider:
-
High Initial Investment: Implementing an ERP system can involve significant upfront costs, including software licensing, hardware upgrades, and implementation services.
-
Complexity and Implementation Time: ERP systems are complex software solutions that require extensive implementation and configuration. The implementation process can be time-consuming and require significant resources.
-
Change Management Challenges: Implementing an ERP system can disrupt existing workflows and require significant changes to business processes. This can lead to resistance from employees and require effective change management strategies.
-
Data Integration and Migration: Integrating data from existing systems and migrating it to the new ERP system can be challenging and time-consuming.
-
Customization and Integration: Customizing an ERP system to meet specific business requirements can be expensive and time-consuming. Integrating the ERP system with other software applications can also pose challenges.
-
Ongoing Maintenance and Support: ERP systems require ongoing maintenance and support to ensure optimal performance and security. This can involve recurring costs for software updates, technical support, and training.
Navigating the ERP Landscape: Choosing the Right System for Your Manufacturing Needs
With a plethora of ERP solutions available, selecting the right one for your manufacturing business can be a daunting task. To make an informed decision, it’s crucial to consider your specific needs, budget, and long-term goals.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing an ERP System
-
Industry-Specific Features: Look for an ERP system that offers features specifically designed for the manufacturing industry, such as production planning, inventory management, and quality control.
-
Scalability and Flexibility: Choose an ERP system that can scale with your business as it grows. It should be flexible enough to accommodate future changes in your operations.
-
Integration Capabilities: Ensure the ERP system integrates seamlessly with your existing software applications, such as CRM, accounting, and warehouse management systems.
-
User-Friendliness and Training: Select an ERP system with an intuitive user interface and comprehensive training resources. This will make it easier for your employees to adopt and use the system effectively.
-
Implementation and Support: Consider the vendor’s experience in implementing ERP systems for manufacturing businesses. Look for a vendor that provides comprehensive implementation services and ongoing support.
-
Cost and ROI: Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including software licensing, implementation, maintenance, and support. Ensure the ERP system offers a strong return on investment (ROI) by improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing profitability.
-
Security and Compliance: Choose an ERP system that meets industry security and compliance standards. It should protect your sensitive data and ensure compliance with regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
Types of ERP Systems for Manufacturing
-
Cloud-Based ERP Systems: Cloud-based ERP systems are hosted on a third-party server, providing access to the software via the internet. They offer scalability, flexibility, and lower upfront costs.
-
On-Premise ERP Systems: On-premise ERP systems are installed and maintained on the company’s own servers. They offer greater control and customization but require significant upfront investment and ongoing maintenance.
-
Hybrid ERP Systems: Hybrid ERP systems combine elements of both cloud-based and on-premise systems, offering a balance of flexibility, control, and cost-effectiveness.
Popular ERP Systems for Manufacturing
-
SAP: SAP is a leading global provider of ERP solutions, offering a wide range of industry-specific modules for manufacturing. SAP systems are known for their scalability, functionality, and comprehensive features.
-
Oracle: Oracle is another major player in the ERP market, offering a comprehensive suite of solutions for manufacturing businesses. Oracle ERP systems are known for their advanced analytics and reporting capabilities.
-
Microsoft Dynamics 365: Microsoft Dynamics 365 is a cloud-based ERP system that offers a user-friendly interface and comprehensive features for manufacturing businesses. It integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products and services.
-
Infor: Infor is a leading provider of industry-specific ERP solutions, including specialized solutions for manufacturing, distribution, and retail. Infor ERP systems are known for their industry expertise and deep vertical market knowledge.
-
Epicor: Epicor is a cloud-based ERP system that offers a wide range of features for manufacturing businesses. It is known for its scalability, flexibility, and ease of use.
Unveiling the Benefits: Real-World Examples of ERP Success in Manufacturing
The transformative power of ERP systems is evident in the success stories of numerous manufacturing businesses. Here are some real-world examples of how ERP systems have helped manufacturers achieve remarkable results:
-
Improved Production Planning and Scheduling: A leading automotive manufacturer implemented an ERP system to streamline its production planning and scheduling processes. The system enabled them to optimize resource allocation, reduce lead times, and improve production efficiency.
-
Enhanced Inventory Management: A food processing company implemented an ERP system to gain better visibility into their inventory levels. The system helped them optimize stock levels, reduce waste, and improve supply chain efficiency.
-
Streamlined Quality Management: A pharmaceutical company implemented an ERP system to improve their quality management processes. The system enabled them to track defects, manage non-conformances, and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
-
Increased Customer Satisfaction: A consumer goods manufacturer implemented an ERP system to improve their order fulfillment processes. The system enabled them to deliver products on time and meet customer expectations, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
-
Reduced Costs and Improved Profitability: A manufacturing company implemented an ERP system to automate tasks, eliminate redundancies, and improve efficiency. The system helped them reduce costs, increase profitability, and gain a competitive advantage.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced ERP Features for Manufacturing
Modern ERP systems offer a range of advanced features that can further enhance efficiency, productivity, and profitability in manufacturing businesses. These features include:
-
Advanced Analytics and Reporting: ERP systems provide advanced analytics and reporting capabilities, enabling manufacturers to gain insights into their operations, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
-
Business Intelligence (BI): BI tools integrated with ERP systems provide real-time dashboards, interactive reports, and predictive analytics, helping manufacturers monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and identify areas for improvement.
-
Internet of Things (IoT): ERP systems can integrate with IoT devices, enabling manufacturers to collect real-time data from machines, sensors, and other equipment. This data can be used to optimize production processes, improve efficiency, and reduce downtime.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered ERP systems can automate tasks, predict demand, and optimize resource allocation. AI algorithms can analyze data, identify patterns, and make recommendations to improve decision-making.
-
Cloud Computing: Cloud-based ERP systems offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. They enable manufacturers to access their data and applications from anywhere, anytime.
-
Mobile Access: Mobile ERP apps enable manufacturers to access key data and perform tasks on their smartphones or tablets. This improves productivity, collaboration, and real-time visibility.
The Implementation Journey: A Step-by-Step Guide to ERP Success
Implementing an ERP system is a significant undertaking that requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing support. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure a smooth and successful implementation:
-
Define Your Business Requirements: Clearly define your business needs and goals for the ERP system. Identify the key processes you want to improve, the data you need to track, and the functionalities you require.
-
Select the Right ERP System: Choose an ERP system that meets your specific requirements, budget, and long-term goals. Consider the vendor’s experience, implementation services, and ongoing support.
-
Develop a Project Plan: Create a detailed project plan outlining the implementation timeline, resources, and milestones. This will help you track progress and ensure the project stays on schedule.
-
Data Migration and Integration: Plan for the migration of data from your existing systems to the new ERP system. Ensure data integrity and accuracy during the migration process.
-
User Training and Adoption: Provide comprehensive training to your employees on how to use the new ERP system. Encourage user adoption and provide ongoing support to address any questions or challenges.
-
Go-Live and Post-Implementation Support: Plan for a smooth go-live process and provide ongoing support to ensure the ERP system operates effectively. Monitor performance, address any issues, and make necessary adjustments.
Navigating the Cost Landscape: Understanding ERP Pricing Models
ERP systems come with a range of pricing models, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these models will help you choose the best option for your business:
-
Subscription-Based Pricing: Subscription-based pricing models involve paying a monthly or annual fee for access to the ERP system. This model offers predictable costs and scalability, as you only pay for the features you use.
-
Per-User Licensing: Per-user licensing models involve paying a fee for each user who accesses the ERP system. This model can be cost-effective for smaller businesses but can become expensive as the number of users increases.
-
On-Premise Licensing: On-premise licensing models involve purchasing a perpetual license for the ERP system. This model requires a significant upfront investment but provides ownership of the software.
-
Implementation Costs: Implementation costs can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the ERP system, the size of your business, and the vendor’s services.
-
Maintenance and Support Costs: Ongoing maintenance and support costs are essential to ensure the ERP system operates effectively. These costs can include software updates, technical support, and training.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What are the essential features of an ERP system for manufacturing?
A1: Essential features include production planning and scheduling, inventory management, quality management, supply chain management, sales and marketing, financial management, and human resources management.
Q2: What are the benefits of implementing an ERP system for manufacturing?
A2: Benefits include improved efficiency and productivity, enhanced visibility and control, better inventory management, improved customer satisfaction, reduced costs, enhanced decision-making, and improved compliance and risk management.
Q3: What are the disadvantages of implementing an ERP system for manufacturing?
A3: Disadvantages include high initial investment, complexity and implementation time, change management challenges, data integration and migration, customization and integration, and ongoing maintenance and support.
Q4: How do I choose the right ERP system for my manufacturing business?
A4: Consider industry-specific features, scalability and flexibility, integration capabilities, user-friendliness and training, implementation and support, cost and ROI, and security and compliance.
Q5: What are the different types of ERP systems for manufacturing?
A5: Types include cloud-based ERP systems, on-premise ERP systems, and hybrid ERP systems.
Q6: What are some popular ERP systems for manufacturing?
A6: Popular systems include SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics 365, Infor, and Epicor.
Q7: How can I ensure a successful ERP implementation?
A7: Follow a step-by-step guide that includes defining business requirements, selecting the right system, developing a project plan, data migration and integration, user training and adoption, and go-live and post-implementation support.
Q8: What are the different ERP pricing models?
A8: Pricing models include subscription-based pricing, per-user licensing, on-premise licensing, implementation costs, and maintenance and support costs.
Q9: What are some advanced ERP features for manufacturing?
A9: Advanced features include advanced analytics and reporting, business intelligence (BI), Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and mobile access.
Q10: What are some real-world examples of ERP success in manufacturing?
A10: Examples include improved production planning and scheduling, enhanced inventory management, streamlined quality management, increased customer satisfaction, and reduced costs and improved profitability.
Q11: How can ERP systems help improve supply chain management?
A11: ERP systems provide tools for supplier management, purchase order processing, and vendor performance tracking, enhancing visibility into the entire supply chain, enabling better collaboration with suppliers, and reducing lead times.
Q12: What are some key considerations for data security and compliance in ERP systems?
A12: Key considerations include data encryption, access control, regular security audits, and compliance with industry regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA.
Q13: How can ERP systems help improve decision-making in manufacturing?
A13: ERP systems provide real-time data and analytics, enabling manufacturers to make informed decisions based on accurate and up-to-date information. They also offer predictive analytics, which can help anticipate future trends and make proactive decisions.
Embark on Your ERP Journey: A Call to Action
The time is now to unlock the potential of your manufacturing business with the power of an ERP system. By carefully considering your specific needs, evaluating different solutions, and implementing the system effectively, you can achieve remarkable results.
Don’t settle for outdated processes and manual workflows. Embrace the transformative power of ERP technology and pave the way for efficiency, growth, and lasting success in your manufacturing operations.
Remember, the right ERP system is more than just software; it’s a strategic investment in your business’s future. Choose wisely, implement with confidence, and watch your manufacturing business thrive!
Disclaimer: This article provides general information about ERP systems for manufacturing and is not intended to be a substitute for professional advice. It is essential to consult with experts and conduct thorough research before making any decisions about ERP implementation. The specific features, benefits, and costs of ERP systems may vary depending on the vendor, industry, and business requirements.
 .
.