Navigating the Complexities of Manufacturing: Unveiling the Power of ERP Systems
 .
.
Welcome to the intricate world of manufacturing, where efficiency, precision, and seamless operations are paramount. In this dynamic landscape, where every cog in the machine must function harmoniously, the role of technology becomes increasingly critical. Enter Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, your trusted ally in streamlining and optimizing your manufacturing processes, from raw material procurement to finished goods delivery.
Imagine a symphony orchestra, each instrument playing its part flawlessly, contributing to a harmonious whole. An ERP system acts as the conductor, orchestrating every aspect of your manufacturing business, ensuring each department, from production and inventory to finance and human resources, plays in perfect sync. This intricate network of interconnected modules, fueled by real-time data, empowers you to gain unprecedented visibility, control, and efficiency across your entire operation.
But the journey towards seamless manufacturing isn’t a straightforward path. Challenges abound, from managing complex supply chains and fluctuating demand to optimizing resource allocation and minimizing production downtime. The sheer volume of data generated within a manufacturing environment can be overwhelming, hindering informed decision-making and hindering productivity. This is where the power of ERP systems truly shines.
By centralizing data across all departments, ERP systems provide a unified platform for real-time insights, empowering you to make data-driven decisions with confidence. With a comprehensive view of your operations, you can anticipate bottlenecks, optimize resource utilization, and proactively address potential issues before they escalate into costly disruptions.
 .
.
ERP systems are not mere data repositories; they are dynamic engines that drive operational efficiency. By automating repetitive tasks, streamlining workflows, and facilitating seamless communication between departments, ERP systems free up your team to focus on higher-value activities, such as innovation and strategic planning.
The benefits of implementing an ERP system extend beyond internal efficiency. By fostering stronger relationships with suppliers and customers, ERP systems create a more collaborative ecosystem. Real-time inventory visibility allows you to meet customer demands promptly, while streamlined communication with suppliers ensures timely delivery of raw materials, minimizing production delays.
In today’s competitive market, agility and adaptability are crucial for survival. ERP systems empower you to react swiftly to changing market conditions, adapting your production plans and strategies to meet evolving customer needs and market trends. This responsiveness allows you to stay ahead of the curve, maintaining a competitive edge in the ever-evolving manufacturing landscape.
Demystifying the Power of ERP Systems: A Comprehensive Guide
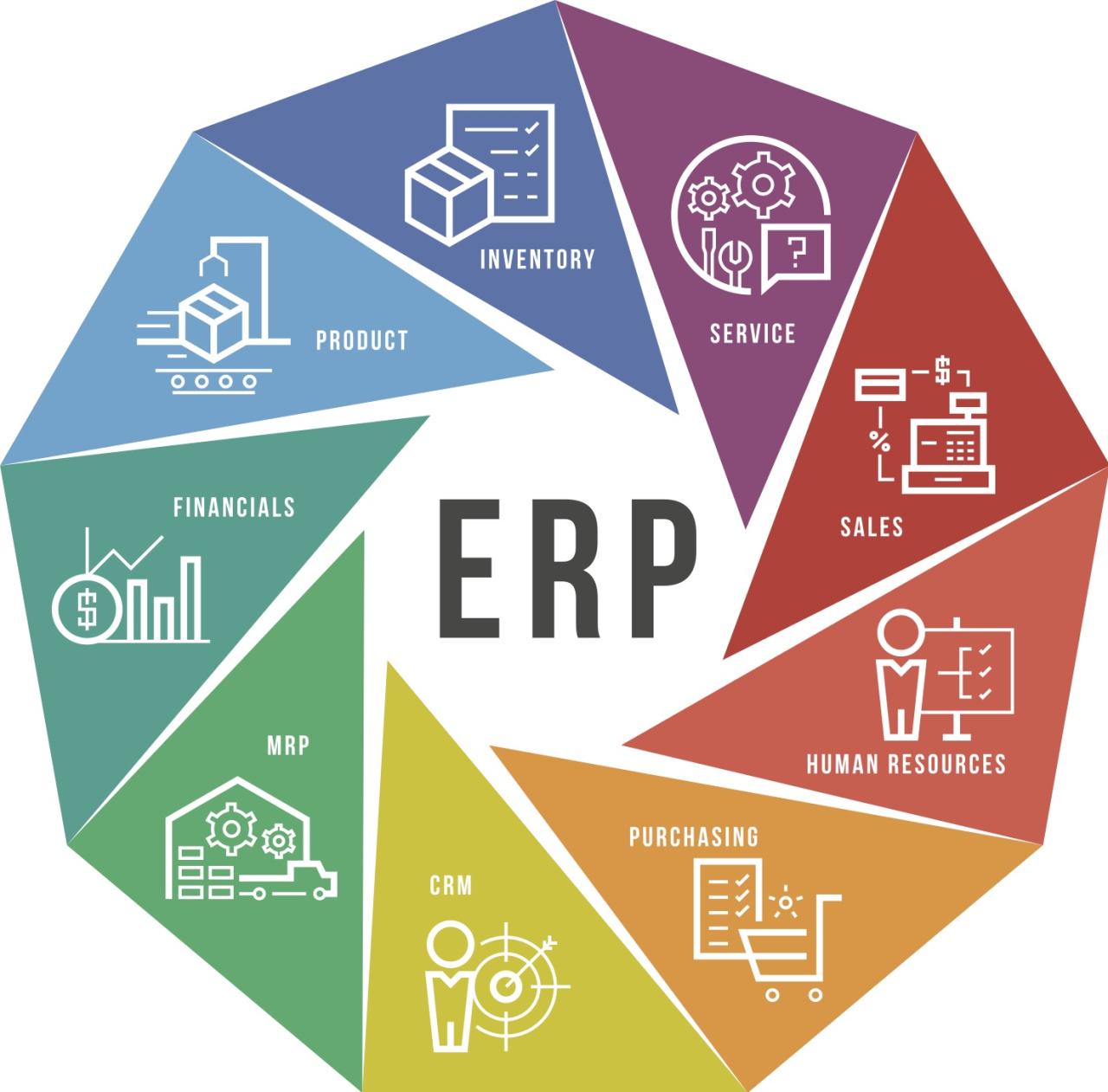
1. Unveiling the Essence of ERP Systems: A Deep Dive into Functionality
ERP systems are not monolithic entities; they are intricate ecosystems composed of interconnected modules, each designed to address specific aspects of your manufacturing operations. This modular structure allows you to tailor your ERP system to meet your unique needs, selecting only the modules that align with your specific business processes.
 .
.
a) Production Planning and Scheduling:
The production planning module acts as the conductor of your manufacturing symphony, orchestrating the entire production process. It empowers you to create detailed production schedules, allocate resources effectively, and track production progress in real-time. By optimizing production schedules and minimizing downtime, this module ensures a smooth flow of goods, maximizing efficiency and productivity.
b) Inventory Management:
Maintaining an optimal inventory balance is a delicate balancing act. The inventory management module provides you with real-time visibility into your inventory levels, allowing you to track stock movements, monitor inventory turnover, and identify potential shortages or overstocking. By automating inventory processes, this module minimizes manual errors, reduces waste, and ensures timely delivery of goods.
c) Quality Control:
 .
.
Maintaining consistent product quality is paramount in manufacturing. The quality control module empowers you to track and manage quality data, identify potential defects, and implement corrective actions. By integrating quality data with other ERP modules, you can proactively address quality issues, reducing production downtime and ensuring customer satisfaction.
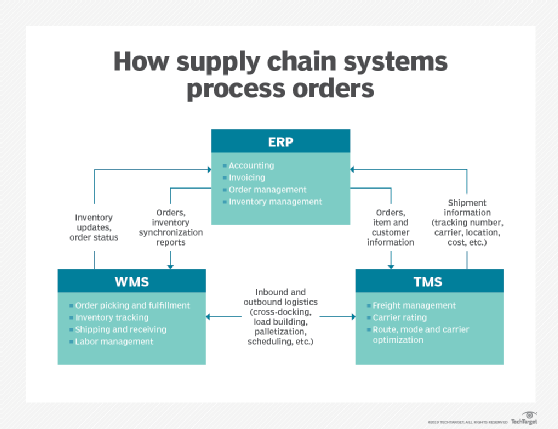
d) Supply Chain Management:
Managing a complex supply chain requires a delicate dance of coordination and communication. The supply chain management module facilitates seamless collaboration with suppliers, enabling you to track orders, monitor delivery schedules, and manage supplier performance. This module ensures a smooth flow of raw materials, minimizing disruptions and optimizing production efficiency.
e) Finance and Accounting:
Financial transparency is crucial for informed decision-making. The finance and accounting module provides comprehensive financial reporting, allowing you to track costs, analyze profitability, and manage cash flow. This module streamlines financial processes, automating tasks like invoicing and payroll, and freeing up your finance team to focus on strategic analysis.
 .
.
f) Human Resources:
Your employees are the backbone of your manufacturing operation. The human resources module empowers you to manage employee data, track performance, and streamline payroll and benefits administration. By automating HR processes, this module frees up your HR team to focus on talent development and employee engagement, fostering a positive and productive work environment.
g) Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
Building strong customer relationships is crucial for long-term success. The CRM module provides a centralized platform for managing customer interactions, tracking sales opportunities, and providing personalized customer service. By integrating with other ERP modules, CRM empowers you to deliver a seamless customer experience, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
2. Exploring the Advantages of ERP Systems: Unlocking Efficiency and Growth
 .
.
ERP systems are not just tools; they are strategic investments that can transform your manufacturing business, driving efficiency, profitability, and sustainable growth.
a) Enhanced Visibility and Control:
ERP systems provide a unified platform for real-time data, giving you a comprehensive view of your entire operation. This visibility allows you to track production progress, monitor inventory levels, and analyze financial performance, empowering you to make informed decisions and proactively address potential issues.
b) Improved Efficiency and Productivity:
By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining workflows, ERP systems free up your team to focus on higher-value activities, such as innovation and strategic planning. This increased efficiency translates into higher productivity, reduced costs, and improved overall performance.
c) Streamlined Decision-Making:
Real-time data insights empower you to make informed decisions based on actual performance data, rather than relying on guesswork or outdated information. This data-driven approach leads to more effective decision-making, minimizing risks and maximizing opportunities.
d) Reduced Costs and Waste:
By optimizing resource allocation, minimizing downtime, and streamlining processes, ERP systems help you reduce production costs and waste. This can significantly improve your bottom line, making your manufacturing operation more profitable and sustainable.
e) Improved Customer Satisfaction:
ERP systems enable you to meet customer demands more effectively, providing timely deliveries and ensuring product quality. This improved customer experience leads to higher satisfaction, increased loyalty, and stronger customer relationships.
f) Enhanced Collaboration and Communication:
ERP systems facilitate seamless communication and collaboration between departments, breaking down silos and fostering a more unified and efficient work environment. This improved communication leads to better coordination, reduced errors, and a more cohesive team dynamic.
g) Increased Agility and Adaptability:
ERP systems empower you to react swiftly to changing market conditions, adapting your production plans and strategies to meet evolving customer needs and market trends. This agility and adaptability are crucial for success in today’s dynamic and competitive manufacturing landscape.
3. Navigating the Challenges of ERP Implementation: Addressing Potential Roadblocks
Implementing an ERP system is a significant undertaking, requiring careful planning, execution, and ongoing maintenance. While the benefits are numerous, potential challenges must be addressed to ensure a successful implementation.
a) Cost of Implementation:
Implementing an ERP system involves significant upfront costs, including software licenses, hardware upgrades, and professional services for implementation and training. It’s crucial to carefully assess the costs involved and develop a realistic budget that aligns with your financial resources.
b) Data Migration and Integration:
Migrating data from existing systems to a new ERP platform can be a complex and time-consuming process. Ensuring data integrity and accuracy is crucial, requiring careful planning and execution to minimize disruptions and ensure a smooth transition.
c) Change Management and User Adoption:
Implementing an ERP system requires significant changes to existing workflows and processes, which can be met with resistance from employees. Effective change management strategies are essential to ensure user adoption and minimize disruption to your operations.
d) Customization and Configuration:
While ERP systems offer a wide range of functionalities, they often require customization and configuration to meet your specific business needs. This customization process can be complex and time-consuming, requiring expertise in ERP implementation and configuration.
e) Ongoing Maintenance and Support:
Once implemented, an ERP system requires ongoing maintenance and support to ensure its functionality and security. This includes software updates, data backups, and technical support to address any issues that may arise.
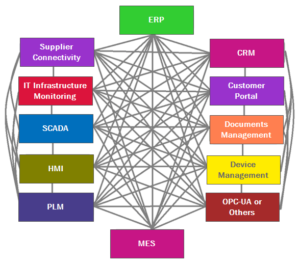
f) Integration with Existing Systems:
Integrating your ERP system with existing systems, such as CRM, accounting software, and warehouse management systems, can be challenging. Ensuring seamless integration is crucial for data flow and overall system efficiency.
g) Data Security and Privacy:
ERP systems contain sensitive data, including financial information, customer data, and employee records. Implementing robust security measures and adhering to data privacy regulations are essential to protect your data and maintain compliance.
4. Selecting the Right ERP System: Tailoring the Solution to Your Needs
With a plethora of ERP systems available, choosing the right solution for your manufacturing business is crucial. Consider these key factors when evaluating different ERP options:
a) Industry-Specific Functionality:
Look for an ERP system designed specifically for manufacturing, offering features tailored to your industry’s unique challenges and requirements. This industry-specific functionality ensures the system aligns with your specific business processes and provides the necessary tools for success.
b) Scalability and Flexibility:
Choose an ERP system that can scale with your business as you grow. This scalability ensures the system can handle increasing data volumes, user accounts, and processing demands without compromising performance.
c) User-Friendliness and Interface:
The user interface should be intuitive and easy to navigate, allowing your team to quickly learn and adopt the system. This user-friendliness ensures efficient adoption and minimizes training requirements.
d) Integration Capabilities:
Consider the system’s ability to integrate with existing systems, such as CRM, accounting software, and warehouse management systems. Seamless integration ensures data flow and optimizes overall system efficiency.
e) Mobile Accessibility:
Look for an ERP system with mobile accessibility, allowing your team to access critical information and perform tasks from anywhere, anytime. This mobility enhances flexibility and productivity, particularly for field-based employees.
f) Cost and Return on Investment (ROI):
Evaluate the total cost of ownership, including software licenses, hardware upgrades, implementation services, and ongoing maintenance. Calculate the potential return on investment, considering the cost savings, increased efficiency, and improved productivity that the ERP system can deliver.
g) Vendor Reputation and Support:
Choose a vendor with a strong reputation for reliability, responsiveness, and customer support. This ensures you have access to the necessary resources to address any issues or challenges that may arise during implementation or ongoing use.
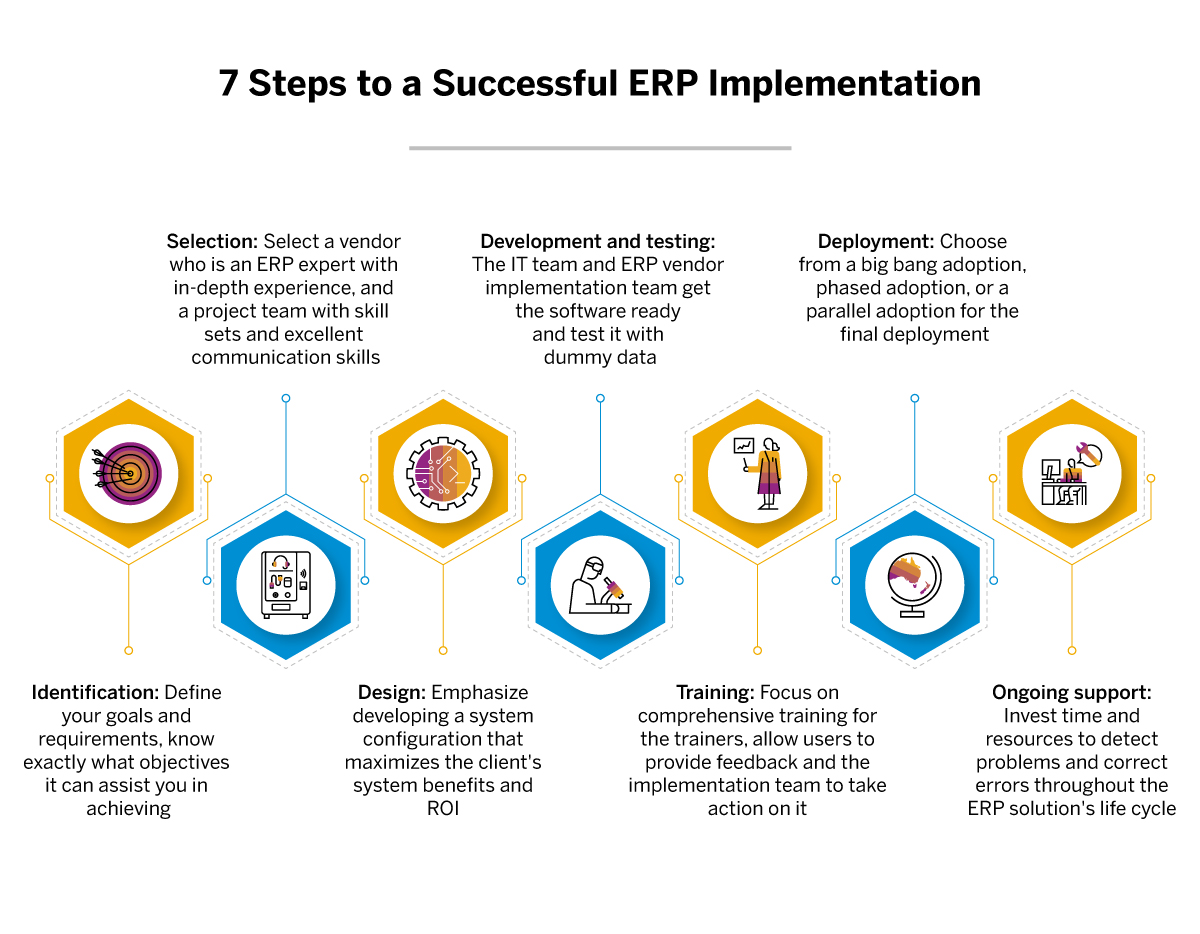
5. Mastering the Implementation Process: Ensuring a Smooth Transition
Implementing an ERP system is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution to ensure a successful transition. Follow these key steps for a seamless implementation:
a) Define Your Business Requirements:
Clearly define your business needs and objectives for the ERP system. This involves identifying key processes, data requirements, and desired outcomes to guide the selection and implementation process.
b) Select the Right ERP System:
Carefully evaluate different ERP options based on your business needs, industry requirements, and budget. Consider factors like functionality, scalability, user-friendliness, integration capabilities, and vendor reputation.
c) Develop a Comprehensive Implementation Plan:
Create a detailed implementation plan outlining timelines, milestones, responsibilities, and resources. This plan should address data migration, user training, system configuration, testing, and go-live procedures.
d) Secure Management Support:
Gain buy-in from key stakeholders and ensure management support throughout the implementation process. This support is crucial for resource allocation, decision-making, and addressing any challenges that may arise.
e) Train Your Users:
Provide comprehensive training to your users on the new ERP system. This training should cover system functionality, navigation, data entry procedures, and best practices.
f) Conduct Thorough Testing:
Perform rigorous testing to ensure the system meets your business requirements and functions as expected. This testing should include data validation, workflow verification, and user acceptance testing.
g) Implement in Phases:
Consider a phased implementation approach, starting with a pilot project to test the system and gather feedback before rolling it out to the entire organization. This phased approach minimizes risk and allows for adjustments based on user feedback.
6. Optimizing Your ERP Investment: Maximizing Return on Investment
Implementing an ERP system is a significant investment, and maximizing its return on investment (ROI) is crucial for success. Here are some strategies to optimize your ERP investment:
a) Continuous Improvement:
Embrace a culture of continuous improvement by regularly reviewing your ERP system usage and identifying areas for optimization. This may involve process improvements, system configuration adjustments, and user training updates.
b) Data Analytics and Reporting:
Leverage the data insights provided by your ERP system to identify trends, analyze performance, and make informed decisions. This data-driven approach enables you to optimize operations, improve efficiency, and drive growth.
c) User Adoption and Engagement:
Encourage user adoption and engagement by providing ongoing support, training, and feedback mechanisms. This fosters a positive user experience and ensures the system is utilized effectively.
d) Integration with Other Systems:
Integrate your ERP system with other business systems, such as CRM, accounting software, and warehouse management systems, to streamline data flow and optimize overall efficiency.
e) Regular Maintenance and Updates:
Ensure your ERP system is regularly maintained and updated to ensure optimal performance, security, and compliance. This includes software updates, data backups, and technical support.
f) Leverage Vendor Resources:
Take advantage of vendor resources, such as training materials, online support forums, and technical support services, to maximize your ERP system’s capabilities and address any issues that may arise.
g) Measure and Track ROI:
Develop key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of your ERP system on your business. Track metrics such as cost savings, increased efficiency, improved productivity, and customer satisfaction to demonstrate the value of your investment.
7. Addressing Common Challenges: Overcoming Implementation Hurdles
Implementing an ERP system can be a complex and challenging process, but with careful planning and execution, you can overcome potential hurdles and achieve a successful implementation.
a) Resistance to Change:
Employees may resist changes to their existing workflows and processes. Address this resistance through effective communication, training, and demonstrating the benefits of the new system.
b) Data Accuracy and Integrity:
Ensuring data accuracy and integrity during migration is crucial. Implement data validation procedures, conduct thorough testing, and involve key stakeholders in the process.
c) System Customization:
Customization can be complex and time-consuming. Clearly define your customization requirements, involve experienced consultants, and prioritize essential functionalities.
d) User Training and Adoption:
Provide comprehensive training, offer ongoing support, and encourage user feedback to foster adoption and maximize system utilization.
e) Integration with Existing Systems:
Thoroughly plan integration with existing systems, involve technical experts, and conduct rigorous testing to ensure seamless data flow and system compatibility.
f) Security and Compliance:
Implement robust security measures, adhere to data privacy regulations, and conduct regular security audits to protect sensitive data.
g) Ongoing Maintenance and Support:
Establish a maintenance plan, schedule regular updates, and ensure access to technical support to address any issues that may arise.
8. Embracing the Future of Manufacturing: ERP Systems as a Catalyst for Innovation
ERP systems are not just tools for managing current operations; they are catalysts for innovation, empowering manufacturers to adapt to changing market conditions, embrace new technologies, and drive sustainable growth.
a) Digital Transformation:
ERP systems are at the heart of digital transformation initiatives, enabling manufacturers to leverage data insights, automate processes, and optimize operations for greater efficiency and agility.
b) Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT):
ERP systems play a key role in integrating Industry 4.0 technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling real-time data collection, predictive maintenance, and smart factory operations.
c) Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
ERP systems can be integrated with AI and ML algorithms to automate tasks, optimize resource allocation, and improve decision-making, driving greater efficiency and profitability.
d) Cloud Computing and Mobility:
Cloud-based ERP systems offer scalability, flexibility, and accessibility, allowing manufacturers to access data and manage operations from anywhere, anytime.
e) Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility:
ERP systems can support sustainability initiatives by tracking energy consumption, optimizing resource utilization, and reducing waste, contributing to a more environmentally responsible manufacturing process.
f) Supply Chain Resilience:
ERP systems enhance supply chain resilience by providing real-time visibility, enabling proactive risk management, and facilitating agile responses to disruptions.
g) Customer-Centric Operations:
ERP systems empower manufacturers to deliver a more personalized and responsive customer experience, leveraging data insights to anticipate customer needs and provide tailored solutions.
9. Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Concerns
Q1: What are the key benefits of implementing an ERP system in a manufacturing environment?
A1: ERP systems offer numerous benefits for manufacturers, including enhanced visibility and control over operations, improved efficiency and productivity, streamlined decision-making, reduced costs and waste, increased customer satisfaction, enhanced collaboration and communication, and greater agility and adaptability.
Q2: What are the common challenges associated with ERP implementation?
A2: Implementing an ERP system can present challenges such as the cost of implementation, data migration and integration, change management and user adoption, customization and configuration, ongoing maintenance and support, integration with existing systems, and data security and privacy.
Q3: How do I choose the right ERP system for my manufacturing business?
A3: Consider factors such as industry-specific functionality, scalability and flexibility, user-friendliness and interface, integration capabilities, mobile accessibility, cost and return on investment, and vendor reputation and support.
Q4: What are the key steps involved in implementing an ERP system?
A4: The implementation process involves defining business requirements, selecting the right ERP system, developing a comprehensive implementation plan, securing management support, training users, conducting thorough testing, and implementing in phases.
Q5: How can I maximize the return on investment from my ERP system?
A5: Optimize your ERP investment by embracing continuous improvement, leveraging data analytics and reporting, fostering user adoption and engagement, integrating with other systems, ensuring regular maintenance and updates, leveraging vendor resources, and measuring and tracking ROI.
Q6: What are some common challenges that manufacturers face during ERP implementation?
A6: Common challenges include resistance to change, data accuracy and integrity, system customization, user training and adoption, integration with existing systems, security and compliance, and ongoing maintenance and support.
Q7: How can ERP systems help manufacturers embrace digital transformation?
A7: ERP systems are at the heart of digital transformation initiatives, enabling manufacturers to leverage data insights, automate processes, and optimize operations for greater efficiency and agility.
Q8: How do ERP systems integrate with Industry 4.0 technologies?
A8: ERP systems play a key role in integrating Industry 4.0 technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling real-time data collection, predictive maintenance, and smart factory operations.
Q9: How can ERP systems leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML)?
A9: ERP systems can be integrated with AI and ML algorithms to automate tasks, optimize resource allocation, and improve decision-making, driving greater efficiency and profitability.
Q10: What are the benefits of cloud-based ERP systems for manufacturers?
A10: Cloud-based ERP systems offer scalability, flexibility, and accessibility, allowing manufacturers to access data and manage operations from anywhere, anytime.
Q11: How can ERP systems support sustainability initiatives in manufacturing?
A11: ERP systems can support sustainability initiatives by tracking energy consumption, optimizing resource utilization, and reducing waste, contributing to a more environmentally responsible manufacturing process.
Q12: How do ERP systems enhance supply chain resilience?
A12: ERP systems enhance supply chain resilience by providing real-time visibility, enabling proactive risk management, and facilitating agile responses to disruptions.
Q13: How can ERP systems help manufacturers deliver a more customer-centric experience?
A13: ERP systems empower manufacturers to deliver a more personalized and responsive customer experience, leveraging data insights to anticipate customer needs and provide tailored solutions.
Embracing the Power of ERP Systems: A Call to Action
The manufacturing landscape is evolving at an unprecedented pace, driven by technological advancements, shifting customer expectations, and a relentless pursuit of efficiency and innovation. In this dynamic environment, ERP systems are not just tools; they are strategic assets that can empower you to navigate the complexities of manufacturing, unlock growth opportunities, and achieve sustainable success.
By embracing the power of ERP systems, you can gain a competitive edge, streamline operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive innovation. The benefits extend far beyond improved efficiency and cost savings; they encompass the ability to adapt to changing market conditions, embrace new technologies, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
The journey towards implementing an ERP system may seem daunting, but with careful planning, expert guidance, and a commitment to continuous improvement, you can overcome challenges and achieve a successful implementation. Remember, an ERP system is not a one-time investment; it’s a strategic partnership that can transform your manufacturing business and propel you towards a brighter future.
Don’t wait for the competition to embrace the power of ERP systems. Take the initiative today and embark on a journey of digital transformation, empowering your manufacturing operation to thrive in the 21st century.
Disclaimer: This article is intended to provide general information and should not be considered professional advice. The information provided is based on industry best practices and research, but specific requirements and challenges may vary depending on your individual business needs. It is recommended to consult with industry experts and conduct thorough research before making any decisions related to ERP implementation.
 .
.
