Unleashing Efficiency: How Small Business ERP Software Can Transform Your Operations
 .
.
Welcome, fellow entrepreneurs! As your business grows, so do the complexities of managing your operations. Juggling inventory, sales, finances, and customer interactions can feel like a constant uphill battle. But what if there was a solution that could streamline these processes, automate tasks, and provide you with real-time insights into your business’s performance? That’s where small business ERP software comes in.
Imagine a single platform that acts as the central hub for all your business activities. This is the power of ERP software. It integrates various departments, from sales and marketing to finance and inventory, providing a unified view of your operations. By eliminating data silos and streamlining workflows, ERP software empowers you to make informed decisions, improve efficiency, and ultimately, achieve greater profitability.
But choosing the right ERP software can be daunting. With a plethora of options available, it’s crucial to understand your specific needs and identify the features that will truly benefit your business. This article will serve as your comprehensive guide to navigating the world of small business ERP software, exploring its advantages, disadvantages, and key functionalities. We’ll also delve into the factors you need to consider when selecting the right solution for your unique business needs.
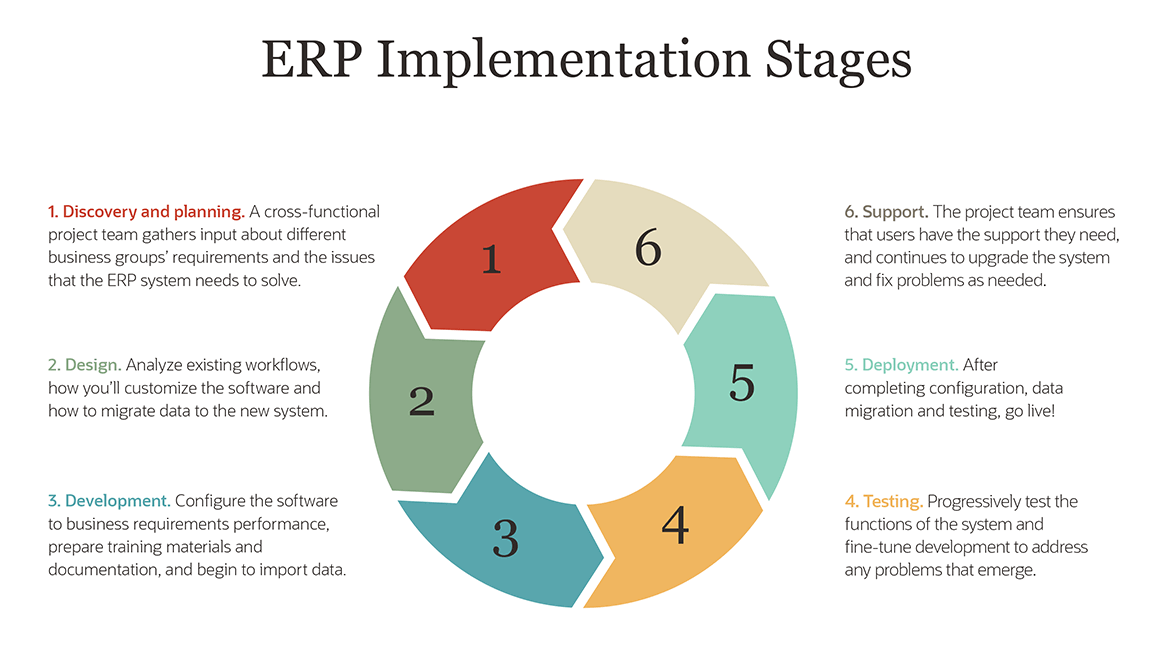
The Rise of Small Business ERP: A Modern Necessity
 .
.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, small businesses face constant pressure to adapt and innovate. Staying competitive requires agility, efficiency, and a deep understanding of your customer base. Traditional methods of managing operations, often relying on disparate spreadsheets and fragmented systems, simply can’t keep up. This is where small business ERP software steps in, offering a modern solution to these challenges.
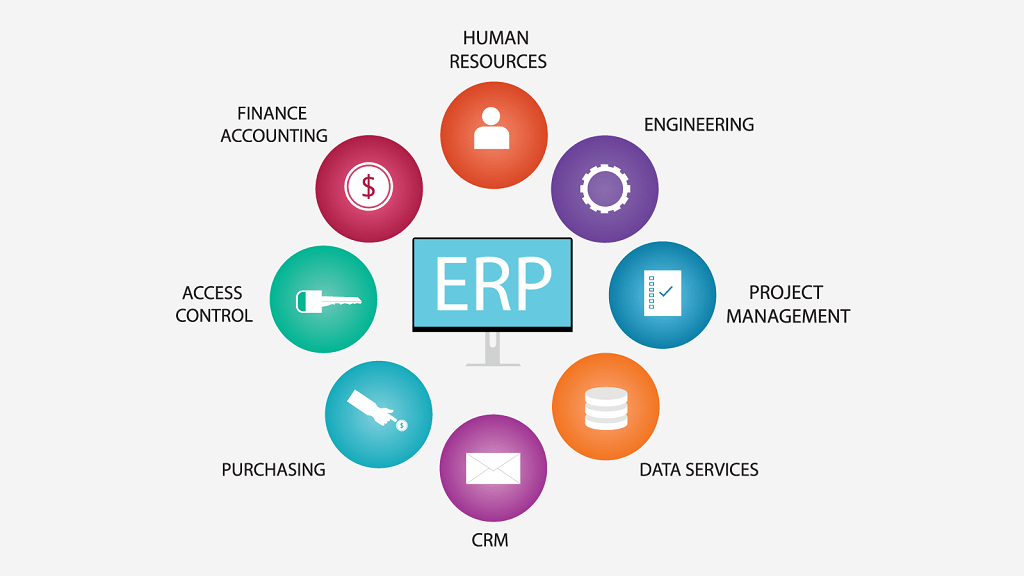
ERP software is designed to empower small businesses by providing a centralized platform for managing all aspects of their operations. By integrating various departments and functions, ERP software eliminates data silos, streamlines workflows, and provides valuable insights into real-time performance. This allows businesses to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and ultimately, drive growth.
Unlocking the Potential: The Advantages of Small Business ERP Software
Small business ERP software offers a wide range of benefits that can significantly impact your bottom line. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity:
ERP software automates repetitive tasks, freeing up your time and resources to focus on strategic initiatives. By streamlining workflows, eliminating manual data entry, and providing real-time insights, ERP software empowers you to achieve greater efficiency and productivity across all departments.
 .
.
2. Improved Data Visibility and Insights:
With a centralized platform for data management, ERP software provides a comprehensive view of your business operations. This allows you to track key metrics, identify trends, and gain valuable insights that inform your decision-making.
3. Streamlined Inventory Management:
ERP software simplifies inventory management by providing real-time visibility into stock levels, purchase orders, and sales history. This helps you optimize inventory levels, reduce stockouts, and minimize storage costs.
4. Enhanced Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
 .
.
Many ERP solutions integrate CRM functionalities, enabling you to manage customer interactions, track sales opportunities, and provide personalized customer service. This fosters stronger customer relationships and drives loyalty.
5. Better Financial Management:
ERP software provides tools for managing accounts payable, accounts receivable, and financial reporting. This allows you to gain better control over your finances, track cash flow, and make informed financial decisions.
6. Scalability and Flexibility:
As your business grows, ERP software can adapt to your changing needs. Most solutions offer scalable options to accommodate increased data volumes, user accounts, and functionalities.
 .
.
7. Improved Collaboration and Communication:
ERP software fosters collaboration by providing a shared platform for communication and information sharing. This reduces silos, improves communication flow, and promotes a more cohesive work environment.
8. Enhanced Security and Compliance:
ERP software typically incorporates robust security features to protect your sensitive data. It also helps you comply with industry regulations and standards, ensuring data integrity and security.
9. Reduced Costs:
 .
.
By automating tasks, streamlining processes, and improving efficiency, ERP software can help you reduce operating costs. This includes minimizing errors, reducing paperwork, and optimizing resource allocation.
10. Increased Profitability:
The combined benefits of efficiency, data visibility, and cost reduction ultimately lead to increased profitability. By making better decisions, optimizing operations, and improving customer satisfaction, ERP software helps you achieve sustainable growth.
Navigating the Landscape: Understanding the Disadvantages of Small Business ERP Software
While ERP software offers numerous advantages, it’s important to be aware of potential drawbacks:
1. Implementation Costs:
Implementing an ERP system can be a significant investment, involving software licensing, customization, training, and ongoing support.
2. Complexity and Learning Curve:
ERP software can be complex, requiring time and effort to learn and master. This can be challenging for small businesses with limited IT resources.
3. Data Migration and Integration:
Migrating data from existing systems to an ERP platform can be a complex and time-consuming process. It’s essential to ensure seamless integration and data accuracy.
4. Customization and Flexibility:
While ERP software offers customization options, it may not always meet all your specific business requirements. This can lead to limitations and potential workarounds.
5. Vendor Dependence:
Choosing an ERP vendor means relying on their support and maintenance. It’s crucial to select a reputable vendor with a strong track record and reliable customer service.
6. Security Risks:
Like any software system, ERP software can be vulnerable to security threats. It’s essential to implement robust security measures to protect your data.
7. Potential for Disruption:
Implementing an ERP system can disrupt daily operations, especially during the initial transition phase. It’s important to plan carefully and minimize disruptions.
8. Ongoing Maintenance and Updates:
ERP software requires ongoing maintenance, updates, and support to ensure optimal performance and security. This can add to the overall cost of ownership.
9. Potential for Over-Customization:
While customization is a valuable feature, excessive customization can make the system more complex and difficult to maintain.
10. Lack of Flexibility:
Some ERP systems may lack flexibility, making it challenging to adapt to changing business needs or industry regulations.
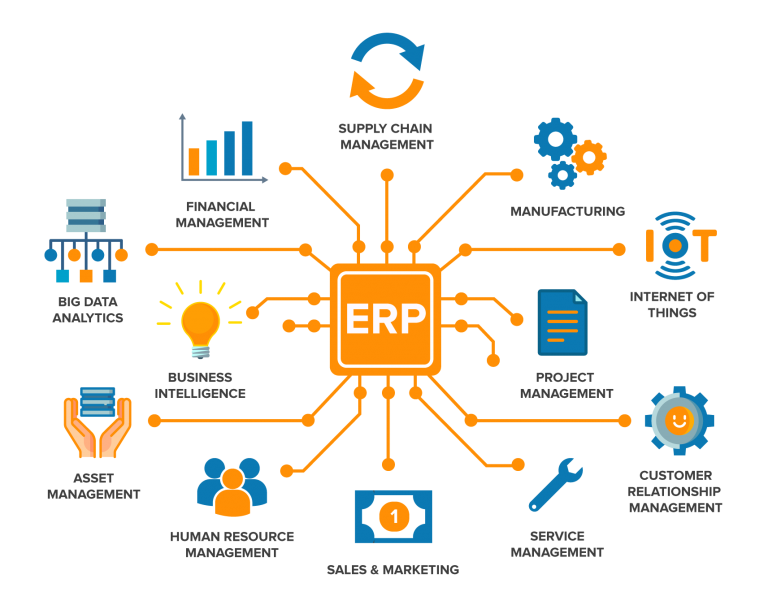
The Essential Elements: Key Features of Small Business ERP Software
Now that we’ve explored the advantages and disadvantages, let’s delve into the key features that make small business ERP software so valuable:
1. Accounting and Financial Management:
ERP software provides robust accounting and financial management capabilities, including:
- Accounts Payable and Receivable: Automate invoice processing, track payments, and manage cash flow.
- Financial Reporting: Generate detailed financial reports, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Create budgets, track expenses, and forecast future financial performance.
2. Inventory Management:
ERP software helps you optimize inventory levels, track stock movements, and manage supplier relationships:
- Stock Tracking: Monitor real-time inventory levels, identify slow-moving items, and prevent stockouts.
- Purchase Order Management: Create and track purchase orders, manage supplier relationships, and negotiate favorable pricing.
- Inventory Forecasting: Predict future demand based on historical data and sales trends.
3. Sales and Marketing:
ERP software integrates sales and marketing functionalities, enabling you to manage customer relationships, track sales opportunities, and streamline marketing campaigns:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Track customer interactions, manage sales pipelines, and personalize customer experiences.
- Sales Order Processing: Automate order entry, manage customer accounts, and track order fulfillment.
- Marketing Automation: Create targeted marketing campaigns, track campaign performance, and measure ROI.
4. Production and Operations Management:
For businesses involved in manufacturing or production, ERP software offers tools for managing production processes, scheduling, and quality control:
- Production Planning: Optimize production schedules, allocate resources, and manage production costs.
- Quality Control: Track product quality, identify defects, and implement corrective actions.
- Work Order Management: Create and manage work orders, track production progress, and ensure timely completion.
5. Human Resources Management:
Some ERP solutions include human resources management functionalities, enabling you to manage employee records, payroll, and benefits:
- Employee Records: Maintain employee information, track attendance, and manage performance reviews.
- Payroll Processing: Automate payroll calculations, manage deductions, and generate paychecks.
- Benefits Administration: Manage employee benefits, track enrollment, and process claims.
6. Reporting and Analytics:
ERP software provides powerful reporting and analytics tools to gain insights into your business performance:
- Dashboard and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Track key business metrics, identify trends, and monitor performance.
- Custom Reports: Generate custom reports based on your specific needs and data requirements.
- Data Visualization: Create interactive dashboards and charts to visualize data and identify patterns.
7. Integration and Customization:
ERP software offers integration capabilities to connect with other business applications, such as accounting software, CRM systems, and e-commerce platforms:
- Third-Party Integrations: Integrate with popular business applications to streamline workflows and data exchange.
- API Connectivity: Access data and functionalities through application programming interfaces (APIs) for custom integrations.
- Customization Options: Tailor the software to meet your specific business requirements and workflows.
8. Mobile Access and Cloud Deployment:
Many ERP solutions offer mobile access, allowing you to manage your business from anywhere, anytime:
- Mobile Apps: Access key features and data through mobile apps for on-the-go management.
- Cloud Deployment: Host your ERP software in the cloud for increased accessibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
9. Security and Compliance:
ERP software typically incorporates robust security features to protect your sensitive data:
- Data Encryption: Encrypt data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Implement user roles and permissions to restrict access to specific data and functionalities.
- Security Audits: Regularly audit your system to identify vulnerabilities and implement necessary security measures.
10. Customer Support and Training:
Choosing an ERP vendor with excellent customer support and training is crucial for successful implementation:
- Technical Support: Access technical support from the vendor to troubleshoot issues and resolve problems.
- User Training: Receive training on the software features, functionalities, and best practices.
- Documentation and Resources: Access comprehensive documentation, tutorials, and online resources for self-paced learning.
Making the Right Choice: Factors to Consider When Selecting Small Business ERP Software
Choosing the right ERP software for your business is a critical decision. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Business Needs and Requirements:
- Industry-Specific Features: Look for software that caters to your specific industry needs, such as manufacturing, retail, or services.
- Scalability and Growth Potential: Ensure the software can accommodate your business growth and future expansion plans.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Consider the software’s ability to integrate with your current accounting, CRM, or e-commerce systems.
2. Budget and Cost Considerations:
- Software Licensing Fees: Determine the cost of software licenses, including annual maintenance and support fees.
- Implementation Costs: Consider the costs of customization, training, and data migration.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculate the potential cost savings and efficiency gains to justify the investment.
3. Vendor Reputation and Support:
- Vendor Experience and Track Record: Choose a reputable vendor with a proven track record of success.
- Customer Support: Evaluate the vendor’s customer support options, including response times, availability, and expertise.
- Training and Resources: Assess the availability of training materials, online resources, and support documentation.
4. User Friendliness and Ease of Use:
- Intuitive Interface: Look for software with a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate and learn.
- Mobile Access: Consider the availability of mobile apps for on-the-go access and management.
- Training and Support: Ensure the vendor provides adequate training and support to help users get up to speed quickly.
5. Security and Compliance:
- Data Encryption: Ensure the software encrypts data at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Access Control: Verify the software offers robust access control features to restrict access to sensitive data.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Confirm the software meets relevant industry standards and regulations.
6. Implementation and Integration:
- Implementation Timeline: Estimate the time required to implement the software and integrate it with existing systems.
- Data Migration: Assess the complexity of data migration from existing systems to the ERP platform.
- Change Management: Plan for change management strategies to minimize disruptions and ensure user adoption.
7. Customization and Flexibility:
- Customization Options: Evaluate the software’s customization options to tailor it to your specific business needs.
- API Connectivity: Consider the availability of APIs for integrating with third-party applications.
- Flexibility to Adapt: Ensure the software can adapt to future changes in your business or industry regulations.
8. Reviews and Testimonials:
- Online Reviews: Read reviews from other users to gain insights into the software’s strengths and weaknesses.
- Testimonials and Case Studies: Review testimonials and case studies to see how other businesses have benefited from the software.
- Industry Forums and Communities: Engage with industry forums and communities to gather feedback and insights from users.
9. Demo and Trial Periods:
- Software Demo: Request a demo from the vendor to see the software in action and get a feel for its interface and features.
- Free Trial Period: Take advantage of free trial periods to test the software in your own environment and assess its suitability.
10. Long-Term Commitment and Support:
- Vendor Stability: Choose a vendor with a long-term commitment to providing support and updates.
- Contractual Agreements: Review the vendor’s contractual agreements, including pricing, support, and maintenance terms.
- Future-Proofing: Consider the software’s long-term viability and its ability to adapt to future technology advancements.
Frequently Asked Questions about Small Business ERP Software
1. What is the best ERP software for small businesses?
The best ERP software for your business depends on your specific needs, budget, and industry. Some popular options include:
- NetSuite: A cloud-based ERP solution with comprehensive features for accounting, inventory, CRM, and more.
- Xero: A cloud-based accounting software with integrated ERP functionalities for small businesses.
- Zoho One: A suite of cloud-based applications, including ERP, CRM, and marketing automation tools.
- SAP Business One: An on-premise ERP solution designed for small and mid-sized businesses.
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central: A cloud-based ERP solution with integrated CRM and financial management capabilities.
2. How much does ERP software cost?
The cost of ERP software varies depending on the vendor, features, and deployment model. Cloud-based solutions typically have monthly subscription fees, while on-premise solutions involve upfront licensing costs. Implementation costs can also vary depending on the complexity of the project.
3. How long does it take to implement ERP software?
The implementation timeline depends on the size and complexity of your business, the chosen software, and the level of customization required. Implementation can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months.
4. What are the benefits of cloud-based ERP software?
Cloud-based ERP software offers several advantages, including:
- Accessibility: Access the software from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Scalability: Easily scale the software to accommodate business growth.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Pay monthly subscription fees rather than upfront licensing costs.
- Automatic Updates: Receive automatic updates and security patches.
5. What are the challenges of implementing ERP software?
Implementing ERP software can present challenges, such as:
- Data Migration: Migrating data from existing systems to the ERP platform.
- User Adoption: Ensuring users are trained and comfortable using the new software.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Integrating the ERP software with other business applications.
- Change Management: Managing the transition to a new system and minimizing disruptions.
6. What are the key features to look for in small business ERP software?
Key features to consider include:
- Accounting and Financial Management: Accounts payable, accounts receivable, financial reporting, budgeting, and forecasting.
- Inventory Management: Stock tracking, purchase order management, inventory forecasting.
- Sales and Marketing: CRM, sales order processing, marketing automation.
- Production and Operations Management: Production planning, quality control, work order management.
- Human Resources Management: Employee records, payroll processing, benefits administration.
- Reporting and Analytics: Dashboards, KPIs, custom reports, data visualization.
- Integration and Customization: Third-party integrations, API connectivity, customization options.
- Mobile Access and Cloud Deployment: Mobile apps, cloud hosting.
- Security and Compliance: Data encryption, access control, compliance with industry standards.
- Customer Support and Training: Technical support, user training, documentation and resources.
7. How can I choose the right ERP software for my business?
Consider the following factors:
- Business needs and requirements: Industry-specific features, scalability, integration with existing systems.
- Budget and cost considerations: Software licensing fees, implementation costs, ROI.
- Vendor reputation and support: Vendor experience, customer support, training and resources.
- User friendliness and ease of use: Intuitive interface, mobile access, training and support.
- Security and compliance: Data encryption, access control, compliance with industry standards.
- Implementation and integration: Implementation timeline, data migration, change management.
- Customization and flexibility: Customization options, API connectivity, flexibility to adapt.
- Reviews and testimonials: Online reviews, testimonials, case studies.
- Demo and trial periods: Software demo, free trial period.
- Long-term commitment and support: Vendor stability, contractual agreements, future-proofing.
8. What are the benefits of using ERP software for small businesses?
ERP software offers numerous benefits for small businesses, including:
- Enhanced efficiency and productivity: Automating tasks, streamlining workflows, and providing real-time insights.
- Improved data visibility and insights: Providing a comprehensive view of business operations and enabling informed decision-making.
- Streamlined inventory management: Optimizing inventory levels, reducing stockouts, and minimizing storage costs.
- Enhanced customer relationship management (CRM): Managing customer interactions, tracking sales opportunities, and providing personalized customer service.
- Better financial management: Managing accounts payable, accounts receivable, and financial reporting.
- Scalability and flexibility: Adapting to changing business needs and growth.
- Improved collaboration and communication: Fostering collaboration and promoting a more cohesive work environment.
- Enhanced security and compliance: Protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
- Reduced costs: Automating tasks, streamlining processes, and improving efficiency.
- Increased profitability: Achieving sustainable growth through better decision-making, optimized operations, and improved customer satisfaction.
9. What are the common mistakes businesses make when choosing ERP software?
Common mistakes include:
- Not defining business needs clearly: Failing to identify specific requirements and goals.
- Focusing solely on price: Choosing the cheapest option without considering long-term value and support.
- Ignoring vendor reputation and support: Neglecting to research the vendor’s track record and customer support capabilities.
- Not involving key stakeholders: Failing to include relevant departments and personnel in the selection process.
- Rushing the implementation process: Implementing the software too quickly without proper planning and training.
- Over-customizing the software: Making excessive customizations that can make the system complex and difficult to maintain.
10. How can I get started with implementing ERP software?
Start by:
- Defining your business needs and goals: Identify your specific requirements and desired outcomes.
- Researching ERP software vendors: Explore different options and compare features, pricing, and support.
- Requesting demos and trial periods: Get a hands-on experience with the software and assess its suitability.
- Involving key stakeholders: Include relevant departments and personnel in the selection process.
- Developing an implementation plan: Outline the timeline, resources, and key milestones.
- Training users and providing support: Ensure users are adequately trained and have access to ongoing support.
Empowering Growth: Taking Action with Small Business ERP Software
As you’ve learned, small business ERP software is a powerful tool that can transform your operations, improve efficiency, and drive profitability. It’s no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses seeking to thrive in today’s competitive landscape.
Don’t let the complexities of managing your business hold you back. Embrace the power of ERP software and unlock its potential to streamline your workflows, enhance data visibility, and empower you to make informed decisions.
Take the first step towards a more efficient and profitable future. Research different ERP software solutions, consider your specific needs, and choose the right platform to drive your business forward.
Disclaimer: This article provides general information about small business ERP software. The specific features, functionalities, and benefits of different ERP solutions may vary. It’s essential to consult with software vendors and conduct thorough research to find the best solution for your business needs. This information is not intended as financial or legal advice.
 .
.
