Headline: Unlock Unprecedented Value: A Comprehensive Guide to ERP Implementation Planning
Introduction:
In today’s fiercely competitive business landscape, organizations are relentlessly seeking ways to optimize their operations, enhance efficiency, and gain a strategic edge. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have emerged as transformative tools in this pursuit, offering a comprehensive solution to streamline processes, centralize data, and empower data-driven decision-making. However, the successful implementation of an ERP system is a complex undertaking that requires meticulous planning and execution. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of ERP implementation planning, providing invaluable insights and actionable steps to ensure a seamless transition and maximize the value of your investment.
Understanding ERP Implementation: A Holistic Approach
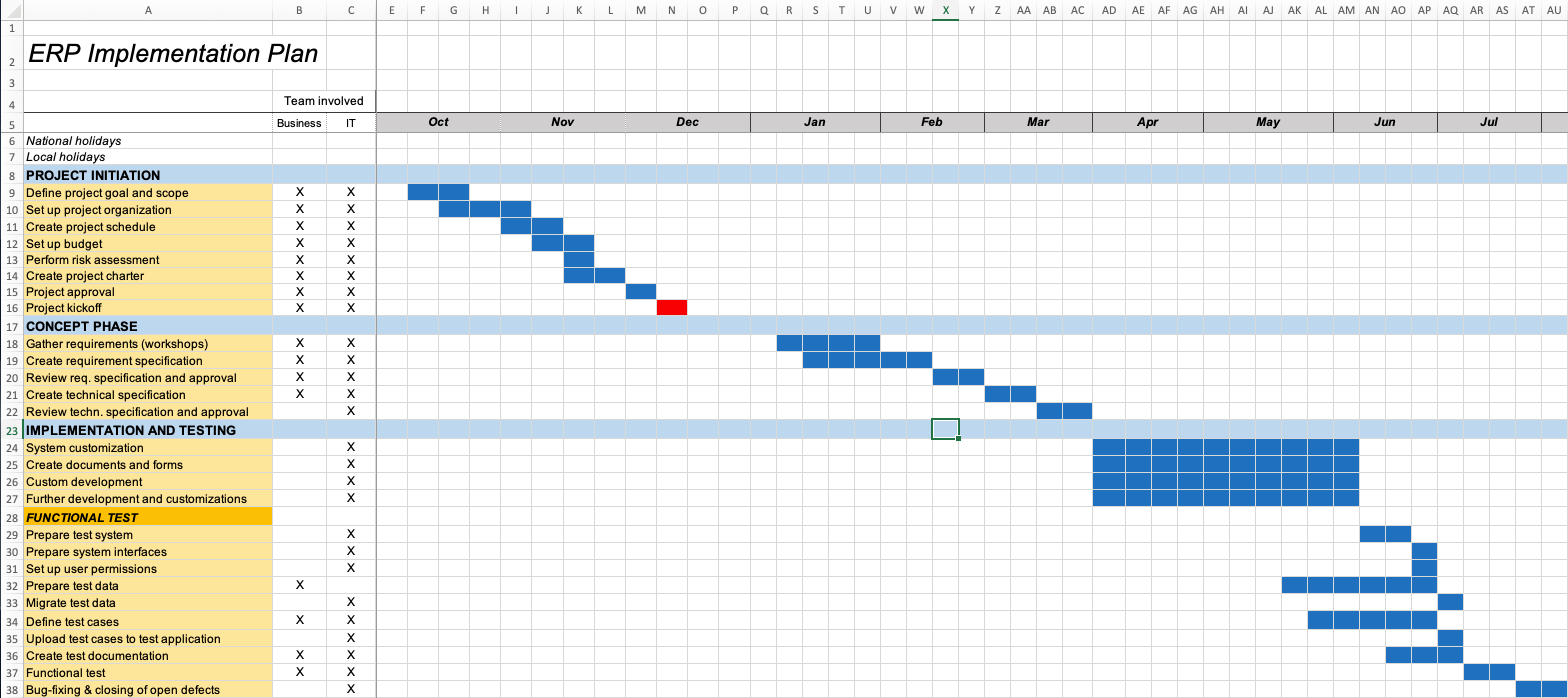
ERP implementation encompasses the comprehensive integration of a software suite that seamlessly connects various business functions, including finance, supply chain management, human resources, and customer relationship management. By consolidating data into a single, centralized repository, ERP systems eliminate data silos, improve collaboration, and provide a holistic view of the organization. The implementation process involves careful planning, customization, data migration, testing, and training to ensure a successful transition.

Key Considerations for ERP Implementation Planning
-
Business Objectives and Scope: Clearly define the specific business objectives that the ERP system aims to address. Determine the scope of the implementation, including the modules and processes to be integrated.
-
Project Management and Governance: Establish a robust project management framework with well-defined roles, responsibilities, and timelines. Implement governance mechanisms to ensure alignment with business goals and stakeholder expectations.
-
Data Management and Migration: Plan for the migration of data from legacy systems to the ERP system. Ensure data accuracy, completeness, and consistency to avoid disruptions during the transition.
-
Customization and Configuration: Tailor the ERP system to meet the specific needs of the organization. Configure workflows, reports, and dashboards to optimize user experience and maximize value.
-
Change Management and Communication: Develop a comprehensive change management strategy to prepare users for the transition. Communicate effectively throughout the implementation process to minimize resistance and ensure buy-in.
-
Testing and Validation: Conduct thorough testing to ensure the accuracy and functionality of the ERP system. Validate the system’s performance against defined requirements and user expectations.
-
Training and Adoption: Provide comprehensive training to users to ensure they are proficient in using the ERP system. Foster adoption through ongoing support, documentation, and knowledge sharing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of ERP Implementation

Advantages:
-
Improved Efficiency and Productivity: ERP systems automate manual processes, streamline workflows, and enhance collaboration, leading to increased efficiency and productivity gains.
-
Centralized Data and Enhanced Reporting: ERP systems provide a single source of truth for all business data, enabling real-time reporting, improved decision-making, and better insights into organizational performance.
-
Reduced Costs and Improved Compliance: ERP systems can reduce operational costs through process optimization and automation. They also facilitate compliance with industry regulations and standards.
-
Increased Agility and Adaptability: ERP systems provide a flexible platform that can be easily adapted to changing business needs and market dynamics.
-
Improved Customer Service and Satisfaction: ERP systems enhance customer service by providing a comprehensive view of customer interactions and enabling proactive issue resolution.
Disadvantages:
-
High Implementation Costs and Complexity: ERP implementation can be a costly and complex undertaking, requiring significant investment in software, hardware, and consulting services.
-
Business Disruption and Downtime: The implementation process can cause temporary disruptions to business operations, leading to potential revenue loss and customer dissatisfaction.
-
Lack of Customization and Flexibility: ERP systems may not be able to accommodate all specific business requirements, leading to the need for customization or integration with other systems.
-
Data Security and Privacy Concerns: ERP systems contain sensitive business data, requiring robust security measures to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
-
Resistance to Change and User Adoption: Users may be resistant to change, making it crucial to implement effective change management strategies to ensure adoption and maximize value.
Summary: Key Points of ERP Implementation Planning
- Define clear business objectives and scope for the ERP implementation.
- Establish a robust project management framework with well-defined roles and responsibilities.
- Plan for data migration and ensure data accuracy and completeness.
- Customize the ERP system to meet specific business needs and optimize user experience.
- Implement a comprehensive change management strategy to prepare users for the transition.
- Conduct thorough testing and validation to ensure system accuracy and functionality.
- Provide comprehensive training and support to ensure user proficiency and adoption.
Q&A: Frequently Asked Questions on ERP Implementation Planning
-
What are the key benefits of ERP implementation?
- Improved efficiency, productivity, and cost reduction
- Centralized data and enhanced reporting
- Increased agility and adaptability
- Improved customer service and satisfaction
-
What are the challenges associated with ERP implementation?
- High implementation costs and complexity
- Business disruption and downtime
- Lack of customization and flexibility
- Data security and privacy concerns
- Resistance to change and user adoption
-
How to plan effectively for ERP implementation?
- Define clear business objectives and scope
- Establish a robust project management framework
- Plan for data migration and ensure data accuracy
- Customize the ERP system to meet specific business needs
- Implement a comprehensive change management strategy
- Conduct thorough testing and validation
- Provide comprehensive training and support
-
What are the best practices for ERP implementation?
- Engage stakeholders early and often
- Establish clear communication channels
- Set realistic expectations and timelines
- Test thoroughly and validate the system
- Provide ongoing training and support
-
What are the common pitfalls to avoid during ERP implementation?
- Underestimating the complexity and cost of implementation
- Lack of stakeholder involvement
- Poor data management
- Insufficient testing and validation
- Resistance to change and user adoption
-
How to measure the success of ERP implementation?
- Define key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Track progress and compare to defined targets
- Gather feedback from users and stakeholders
- Evaluate the impact on business outcomes
-
What are the emerging trends in ERP implementation?
- Cloud-based ERP systems
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML)
- Integration with other business systems
- Mobile and remote access
-
How to choose the right ERP vendor and solution?
- Define your business requirements
- Research and evaluate different vendors
- Request demos and references
- Consider the vendor’s experience and expertise
-
What are the different types of ERP implementation methodologies?
- Big bang approach
- Phased approach
- Parallel approach
- Pilot approach
-
How to manage change effectively during ERP implementation?
- Communicate the benefits and impact of the change
- Involve stakeholders in the planning process
- Provide training and support
- Monitor progress and address resistance
-
What is the role of leadership in ERP implementation success?
- Provide vision and direction
- Engage stakeholders and build consensus
- Remove obstacles and provide support
- Celebrate successes and learn from mistakes
-
How to ensure data integrity during ERP implementation?
- Establish data governance policies
- Implement data validation and cleansing processes
- Back up data regularly
- Monitor data quality and integrity
-
What are the legal and regulatory considerations for ERP implementation?
- Comply with industry regulations and standards
- Protect sensitive data and ensure privacy
- Consider the impact on contracts and agreements
Conclusion:
ERP implementation is a transformative journey that can unlock unprecedented value for organizations. By carefully planning and executing the implementation process, businesses can reap the benefits of improved efficiency, enhanced decision-making, and increased competitiveness. Embrace the challenges and opportunities that come with ERP implementation, and seize the opportunity to revolutionize your business operations.
Closing Statement:
The successful implementation of an ERP system is a testament to the power of strategic planning, collaboration, and unwavering commitment. Remember, the journey is as important as the destination. Embrace the challenges, learn from your experiences, and continuously strive for excellence. With the right approach and a relentless pursuit of value, your ERP implementation will be a resounding success, propelling your organization to new heights of performance.
