SAP vs. ERP: Unveiling the Value Proposition for Your Ideal Customer
In the ever-evolving landscape of business technology, the terms SAP and ERP often emerge as key players in the quest for operational efficiency and growth. While both systems aim to streamline processes and provide valuable insights, their distinct offerings cater to specific needs and pain points. This comprehensive blog post delves into the intricacies of SAP vs. ERP, empowering you to make an informed decision for your organization.
Understanding SAP: The Enterprise Giant
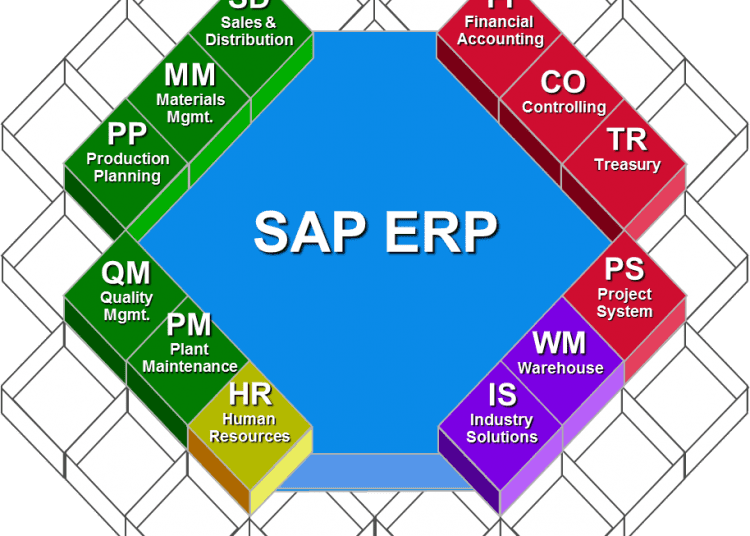
SAP, short for Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing, is a comprehensive enterprise resource planning (ERP) software suite designed to integrate and manage various aspects of a business. Its modular architecture allows organizations to tailor the system to their specific requirements, covering a wide range of functional areas including finance, human resources, supply chain management, and customer relationship management (CRM). SAP’s strength lies in its ability to provide a single, centralized platform for managing complex business processes, facilitating seamless data flow and eliminating the need for disparate systems.
ERP: The Backbone of Business Operations
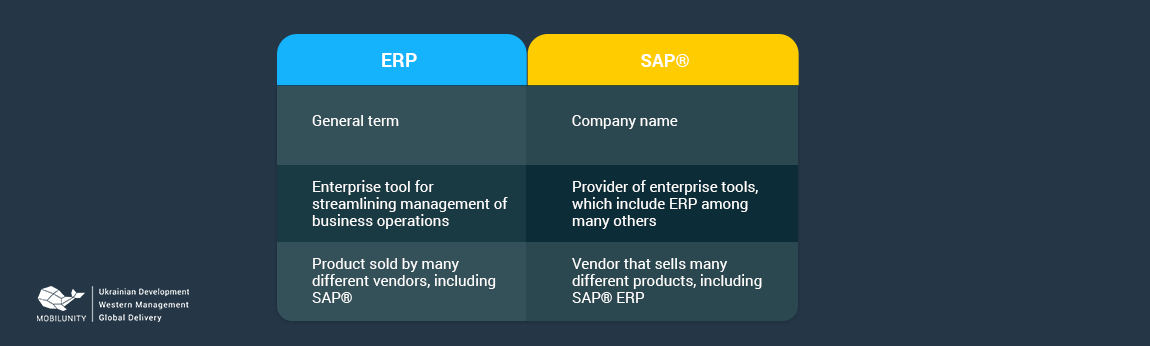
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, like SAP, serve as the backbone of many organizations, providing a comprehensive suite of integrated applications that streamline and automate business processes. ERP systems centralize data and provide real-time visibility into various aspects of the organization, enabling informed decision-making and improved operational efficiency. By integrating key business functions, ERP systems eliminate data silos, reduce redundancy, and enhance collaboration across departments.
SAP vs. ERP: A Comparative Analysis
While SAP and ERP often overlap in terms of functionality, they differ in certain key aspects that may influence your choice.
1. Scope and Complexity: SAP is a highly comprehensive ERP suite that caters to the needs of large enterprises with complex business processes. Its modular architecture allows for extensive customization and integration, making it suitable for organizations with diverse and demanding requirements. ERP systems, on the other hand, may offer a more focused range of functionality, catering to the needs of smaller businesses or specific industries.
2. Cost and Implementation: SAP implementations are typically more expensive and time-consuming compared to ERP systems. The complexity of SAP and the need for extensive customization require specialized expertise and resources, which can drive up the overall cost of implementation. ERP systems, with their more streamlined functionality, may offer a more cost-effective and less resource-intensive implementation process.
3. Industry Specialization: SAP offers industry-specific solutions tailored to the unique requirements of various sectors, such as manufacturing, retail, and healthcare. This industry-specific focus enables SAP to provide tailored functionality and best practices that align with the specific challenges and opportunities of each industry. ERP systems, while not as industry-specific, may offer add-on modules or integrations that cater to certain industry requirements.
4. Scalability and Flexibility: SAP’s modular architecture provides scalability and flexibility, allowing organizations to start with a core set of modules and gradually expand the system as their needs evolve. ERP systems may offer less flexibility in terms of customization and scalability, as they are often designed to meet the needs of a specific size or industry segment.
5. Integration and Interoperability: SAP offers a wide range of integration options, enabling seamless connectivity with other systems and applications. Its open architecture and extensive ecosystem of partners facilitate the integration of third-party solutions and custom developments. ERP systems may have more limited integration capabilities, which can impact the ability to connect with other systems and extend functionality.
6. User Interface and Usability: SAP’s user interface has evolved over the years, offering a more intuitive and user-friendly experience. However, due to its complexity, SAP may require specialized training and support for users to fully leverage its capabilities. ERP systems may offer a simpler and more streamlined user interface, making them easier to adopt and use for non-technical users.
Advantages and Disadvantages of SAP vs. ERP
Advantages of SAP:
1. Comprehensive Functionality: SAP’s comprehensive suite of modules covers a wide range of business functions, providing a single, integrated platform for managing all aspects of an organization.
2. Industry Specialization: SAP offers industry-specific solutions tailored to the unique requirements of various sectors, providing tailored functionality and best practices.
3. Scalability and Flexibility: SAP’s modular architecture allows for scalability and flexibility, enabling organizations to start with a core set of modules and gradually expand the system as their needs evolve.
4. Integration and Interoperability: SAP offers a wide range of integration options, enabling seamless connectivity with other systems and applications.

5. Strong Ecosystem: SAP has a strong ecosystem of partners and developers, providing access to a wide range of add-on solutions and industry expertise.
Disadvantages of SAP:
1. Cost and Implementation: SAP implementations are typically more expensive and time-consuming compared to ERP systems.
2. Complexity: SAP’s comprehensive functionality and modular architecture can make it complex to implement and use, requiring specialized expertise and resources.
3. Customization: SAP’s extensive customization options can be a double-edged sword, as it may require significant time and resources to tailor the system to specific requirements.
4. Limited Flexibility: While SAP offers scalability, it may not be as flexible as some ERP systems in terms of adapting to changing business needs.
5. User Interface: SAP’s user interface, while improved, can still be complex and require specialized training for users to fully leverage its capabilities.
Advantages of ERP:
1. Cost-Effectiveness: ERP systems are typically more cost-effective to implement and maintain compared to SAP, making them a more viable option for small and medium-sized businesses.
2. Streamlined Functionality: ERP systems offer a more focused range of functionality, making them easier to implement and use for organizations with less complex business processes.
3. User-Friendliness: ERP systems often have a simpler and more intuitive user interface, making them easier to adopt and use for non-technical users.
4. Flexibility: ERP systems may offer greater flexibility in terms of customization and scalability, enabling organizations to adapt the system to their specific needs and changing business environment.
5. Industry-Specific Solutions: While not as industry-specific as SAP, ERP systems may offer add-on modules or integrations that cater to the unique requirements of certain industries.
Disadvantages of ERP:
1. Limited Functionality: ERP systems may not offer the same level of comprehensive functionality as SAP, which can be a limitation for organizations with complex business processes.
2. Integration Challenges: ERP systems may have more limited integration capabilities, which can impact the ability to connect with other systems and extend functionality.
3. Scalability: ERP systems may not be as scalable as SAP, which can limit their ability to support the growth and evolving needs of large enterprises.
4. Industry Specialization: ERP systems may not offer the same level of industry-specific functionality and expertise as SAP, which can be a disadvantage for organizations operating in highly specialized industries.
5. Customization: ERP systems may offer less flexibility in terms of customization compared to SAP, which can limit the ability to tailor the system to specific requirements.
Summary of SAP vs. ERP
SAP and ERP systems offer distinct advantages and disadvantages, catering to different organizational needs and pain points. SAP is a comprehensive ERP suite ideal for large enterprises with complex business processes and a need for industry-specific functionality. ERP systems, on the other hand, are more cost-effective and streamlined, making them a suitable choice for small and medium-sized businesses or organizations with less complex requirements.
Q&A
1. What is the primary difference between SAP and ERP?
SAP is a comprehensive ERP suite designed for large enterprises, while ERP systems offer a more focused range of functionality suitable for smaller businesses or specific industries.
2. Which system is more cost-effective?
ERP systems are typically more cost-effective to implement and maintain compared to SAP.
3. Which system is more user-friendly?
ERP systems often have a simpler and more intuitive user interface compared to SAP.
4. Which system is more flexible?
ERP systems may offer greater flexibility in terms of customization and scalability compared to SAP.
5. Which system offers better industry specialization?
SAP offers industry-specific solutions tailored to the unique requirements of various sectors, while ERP systems may offer add-on modules or integrations for specific industries.
6. What are the key advantages of SAP?
Comprehensive functionality, industry specialization, scalability, integration capabilities, and a strong ecosystem.
7. What are the key disadvantages of SAP?
Cost and implementation complexity, customization challenges, limited flexibility, and a complex user interface.
8. What are the key advantages of ERP systems?
Cost-effectiveness, streamlined functionality, user-friendliness, flexibility, and industry-specific solutions.
9. What are the key disadvantages of ERP systems?
Limited functionality, integration challenges, scalability limitations, less industry specialization, and reduced customization options.
10. Which system is better suited for large enterprises?
SAP is better suited for large enterprises with complex business processes and a need for industry-specific functionality.
11. Which system is better suited for small and medium-sized businesses?
ERP systems are better suited for small and medium-sized businesses or organizations with less complex requirements.
12. Can ERP systems be customized?
Yes, ERP systems offer customization options, but they may not be as extensive as SAP’s customization capabilities.
13. How do I choose between SAP and ERP?
Consider your organization’s size, industry, business processes, budget, and long-term goals to determine which system best aligns with your needs.
Conclusion
The choice between SAP and ERP is a strategic decision that requires careful consideration of
